作者简介:戴彩丽(1971—), 中国石油大学(华东)教授、博士生导师. 研究方向:采油化学、提高采收率理论与技术、非常规能源高效开发. E-mail:daicl306@163.com
中文责编:晨 兮; 英文责编:天 澜
1)中国石油大学(华东)山东省油田化学重点实验室,山东青岛 266580; 2)中国石油大学(华东)非常规油气开发教育部重点实验室,山东青岛 266580; 3)中国科学技术大学工程科学学院,安徽合肥 230027; 4)中国石油勘探开发研究院,北京 100083
1)Shandong Key Laboratory of Oilfield Chemistry, China University of Petroleum(East China), Qingdao 266580, Shandong Province, P.R.China;2)Key Laboratory of Unconventional Oil & Gas Development, China University of Petroleum(East China), Qingdao 266580, Shandong Province, P.R.China;3)School of Engineering Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, Anhui Province, P.R.China;4)PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development, Beijing 100083, P.R.China
oil and gas well development engineering; enhanced oil recovery; micro-nano pores; nanomechanical technology; molecular dynamics; oil adhesion mechanism; displacement efficiency; interface interaction
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.06551
2020年中国原油对外依存度高达73%,远超国际公认的50%安全警戒线,油气供给面临极大挑战[1-2].中国低渗和特低渗石油资源丰富,在鄂尔多斯盆地、松辽盆地、四川盆地和松辽盆地等盆地均有分布,新探明储量超80亿t,占总探明储量70%以上, 成为我国油气增储上产的 “主力军”[3-5].
低渗和特低渗储层微纳米级孔喉发育,80%以上可动原油储集于孔径为0.01~10.00 μm的孔隙中,依靠天然能量开采,产能低且产量递减快,常通过注水提高产量[6-7].然而,由于低渗和特低渗储层孔隙小,比表面积大,原油与岩石壁面直接接触且受壁面束缚占比远高于常规储层,水驱过程中微纳孔隙黏附的油膜难以剥离启动,导致洗油效率远低于50%[8-11].此外,微纳孔隙中黏附的油膜(厚度可达孔隙直径的29%~36%)大幅降低了基质的有效孔隙度和水相相对渗透率,致使注水时压力上升快,地层能量补充困难[12-13].可见,油膜黏附问题极大限制了低渗和特低渗油藏的开发效率.
传统理论认为,注入流体的洗油效率取决于原油在岩石壁面的黏附功,黏附功越低,洗油效率越高.黏附功W为
W=σ(1+cos θoil)(1)
其中, σ为油水界面张力; θoil为油相接触角.大幅降低油水界面张力即可显著减小油膜黏附功,提升油膜剥离效率[14].这一理论对常规油田的开发具有重要的指导意义[15-18].在大庆、胜利和渤海等油田常规储层,通过添加表面活性剂及碱使油水界面张力降至超低(<0.01 mN/m),大幅提升了油膜剥离效果,提高了产量.然而,在低渗和特低渗储层,即使油水界面张力降至超低,驱替后仍有大量油膜残存在微纳孔隙壁面[19](图1).该现象表明黏附功理论不足以阐明油膜岩壁黏附机理.
图1 表面活性剂驱替后油膜残留岩石表面示意图[19]
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of residual oil film on rock surface after surfactant displacement[19]
图1 表面活性剂驱替后油膜残留岩石表面示意图[19]
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of residual oil film on rock surface after surfactant displacement[19]
胶体与界面科学中经典Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey Overbeek(DLVO)理论已被广泛应于描述胶体粒子在水中的稳定性,该理论认为粒子间因范德华作用而相互吸引,又因扩散双电层的重叠而互相排斥.根据DLVO理论,若油膜与岩壁间仅存在范德华和双电层作用,二者合力表现为弱引力甚至斥力[14,17],注水开发应具有较高洗油效率.但对原油-岩石来说,实际采收率却远低于预期[19],说明经典DLVO理论对原油-岩石间相互作用力解析也不全面,存在非DLVO理论的强相互作用使油膜黏附在岩石壁面难以剥离.油膜-岩石间强相互作用成为低渗、特低渗储层制约油膜剥离效率、影响最终采收率的主要因素.本文总结了近年来油-水-岩石微观界面相互作用及原油岩壁黏附机理的研究进展,简要介绍了微观界面力学解析手段,论述了原油-岩石间DLVO相互作用(范德华力和双电层力)及非DLVO相互作用(疏水作用力和离子桥连作用等)的主要研究成果,并对该领域目前面临的挑战以及应用前景进行了展望.
探明低渗和特低渗油藏油膜剥离机理,透彻地理解油膜黏附界面力学机理是基础,明确油膜黏附关键作用位点及其破坏机制是核心.传统的动静态接触角及界面张力等研究方法往往是一定区域内统计的宏观平均值,对于组成复杂的岩石表面微观形貌,无法反映微纳孔隙中油滴真实铺展状态、定量预测微纳米级表面力分布,因此,需要利用纳米力学技术(精度1 pN或1×10-10 m)量化解析微纳尺度原油-岩石间分子力[14,20,21-27],阐明油-水-岩石微观界面相互作用机制.
原子力显微镜(atomic-force microscope, AFM)液滴探针技术、化学力探针技术及表面力仪(surface-force apparatus, SFA)作为纳米力学重要研究手段备受关注(图2).SFA技术最早用于在真空或气体中测量光滑云母表面之间的表面力,后被拓展至材料、生物和工程等领域进行表面力测量[20].SFA可实现不同表面间相互作用力与界面间绝对距离的高精度测量,但要求被测表面具有透光性且相对光滑,一定程度上制约了其在工程领域中的应用范围[25-28].
1981年BINNING等[29]发明了扫描隧道显微镜(scanning tunneling microscope, STM),用于固体表面的原子级成像.1982—1986年,在STM的基础上进一步开发了AFM,从此AFM被广泛用于形貌探测以及真空、气体和液体介质中多种材料的力学测量[30].目前,已经开发了包括化学力探针、胶体探针、液滴或气泡探针等多种AFM探针.相较于SFA,AFM对所要检测表面没有透光的限制.通过耦合AFM液滴探针、雷诺润滑理论和杨-拉普拉斯方程的理论模型,可获得高精度柔性(可变形)界面间力-距离曲线,能够直接测量和分析油-水-固三相体系中各种分子间和界面间作用力(如范德华力、双电层力、疏水作用、氢键、阳离子-π电子云作用和纳米润滑等),因此,更适用于原油-岩石间相互作用纳米力学特性分析.
除纳米力学实验测量以外,分子动力学模拟也是解析微观作用力的重要手段之一,它是一种研究分子及原子体系中粒子运动的计算机模拟方法.在模拟时间范围内,分子或原子之间通过分子力场产生相互作用从而发生运动,运动轨迹受牛顿运动规律控制.在此过程中,体系总能量为动能与势能(包括分子间作用力引起的势能和分子内部势能)之和.通过数值求解可得到体系中粒子的位置、速度及受力情况等随时间的演化信息,从而预测体系热力学及其他宏观性质[29-30].
图3 离子在油-水-固三相体系中微观构象分子模拟示意图
Fig.3 Molecular dynamic simulation of ions in oil-water-solid three phase system
分子动力学模拟(图3)一方面可计算油-水-岩石三相体系各组分间的相互作用力,与实验相互验证校准,另一方面能从分子尺度模拟油-水-岩石三相体系中界面的微观构象演化过程[31-34],分析不同时刻界面处烷烃分子、离子和水等排布规律,得到界面微观构象和界面处作用力的耦合关系,从分子尺度识别出强相互作用的微观表现形式[14,28].
在低渗、特低渗油藏注水开发过程中,岩石颗粒孔隙中的油滴、附着在岩壁上的油膜、水膜以及地层水构成了油-水-岩石体系,体系三相界面间存在相互作用.目前关于原油-岩石间相互作用力的研究表明,由于原油中的极性物质的解离,油-岩间不仅存在包含双电层力[35-40]和范德华力[20-42]在内的经典DLVO相互作用,也存在其他非DLVO相互作用,例如疏水相互作用[22, 28]和离子桥连作用[31-33]等,导致注水开发后仍有大量残余油膜黏附在岩石壁面难以剥离.
双电层力(electric double-layer force, EDL)是液体中(特别是极性溶剂中, 比如水)两带电体之间的相互作用力,其力程为纳米级,大小随带电体表面电荷密度或表面电势的增大而增大.
在低渗和特低渗储层中,砂岩黏土颗粒由于晶格取代和电离作用,表面往往带负电,而由于极性物质的解离作用,原油表面通常也带负电.在水溶液中,带电表面上的电荷会被等量与之相反的电荷(反离子)所平衡.反离子一方面受静电作用趋于向带电表面靠近,另一方面受分子热运动及扩散作用的影响趋于在体相中分布.在两种作用协同下,溶液中的带电表面附近形成双电层结构,一层是紧靠表面的反离子形成的紧密层,其厚度由吸附离子大小决定; 另一层是其他反离子以快速布朗运动分布在表面附近的扩散层.两带电体的电势会造成离子不均匀分布,从而形成渗透压,成为岩石、黏土矿物与原油之间相互作用的来源.两个带相同电荷的带电体之间的双电层力为斥力,斥力随二者间距呈指数衰减; 当两带电体所带电荷不等且间距较小时,双电层力有可能是吸引力.
假设表面电位不变的情况下,水介质中两个不同形状几何体间双电层作用力和能量可以用粒子、相互作用常数Z和德拜长度κ-1表示,如表1[20]. 其中, z1和z2为2种电解质价态; ε0和ε分别为体相和介质的介电常数; D为两几何体间隔距离; R为物体半径; A为Hamaker常数, A=π2Cρ1ρ2, ρ1和ρ2分别是两物体单位体积原子数量; σ为表面电荷密度; C为原子与原子之间的二体势能.
表1 用Hamaker常数A表示的不同几何体间范德华和双电层相互作用表达[20]
Table 1 Expression of VDW and EDL interactions among different geometries expressed by Hamaker constant A[20]
双电层相互作用常数Z为
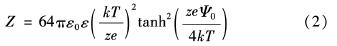
其中, z为电解质价态; Ψ0为电位; T为热力学温度.式(2)表明Z受溶液中电解质的表面性质和价态影响; 德拜长度表示双电层相互作用的衰变长度,它取决于温度、电解液类型和电解液浓度,并随离子浓度和价态的增高而减小.
在图4[33]的油-水-固系统中, Φ为stern面的电势, ξ1和ξ2分别为滑动面与溶液内部的电势; h为两界面的滑动面间距.双电层力的强度主要由双电层的厚度和表面电荷量决定,双电层的厚度和表面电荷量取决于地层水的离子组成、价态和浓度. BUCKLEY等[35]利用双电层排斥理论预测了原油在不同pH值和NaCl浓度下与二氧化硅的黏附性,但未能解释高浓度NaCl溶液中原油不黏附的原因.HIRASAKI[36]构建了系统的框架来计算表面力(范德华力和双电层斥力)对接触角的影响.TIAN等[33, 37]报道,在砂岩中黏土与原油之间的双电层排斥作用受地层水浓度影 响,它可能会改变油-水-固系统的润湿性,从而对残余油膜的剥离产生影响(图5).随后,一些研究报道了润湿性随盐度的变化趋势[38- 40].MAHANI团队[40]研究认为储层中黏土形态会增强双电层排斥效应.而当原油与岩石表面电荷相反时,高盐度会导致亲水性增强[41].
图4 油-岩间双电层力示意图[33]
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of double electric layer force between oil and rock[33]
范德华相互作用起源于两个分子相互接近时的波动电偶极矩,主要包括色散力(瞬时偶极之间的电性引力)、取向力(固有偶极之间的电性引力)和诱导力(诱导偶极与固有偶极之间的电性引力),因此,范德华力在所有分子和表面之间无处不在[42].无论油-水-固系统中的界面电荷和组分如何,范德华力的普遍存在,对黏附、润湿和吸附等现象的研究具有重要影响.
图5 原油-黏土间双电层排斥示意图[33]
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of double electric layer repulsion between oil and clay[33]
表1中总结了间隔为的两个不同几何体之间的范德华相互作用能和力的表达式(以Hamaker常数A表示).范德华相互作用随距离呈幂律衰减,且对不同几何形状有不同指数.
基于范德华力的Lifshitz理论,将宏观相视为连续介质.非阻滞Hamaker常数A可以用式(3)介质特性表示.如果3种介质吸收频率相同,则对于通过介质. 其中, n1、n2和n3分别为3种介质的折射率; ε1、ε2和ε3分别为3种介质的介电常数.如果3种介质的吸收频率相同,则对于通过介质3相互作用的宏观介质1和介质2的Hamaker常数A132[20] 为
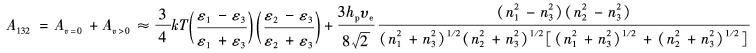 (3)
(3)
其中, k为玻耳兹曼常数; υe为3×1015 Hz附近紫外段的主电子吸收频率; hp为普朗克常数.
穿过介质3的两个相相同时,对应的Hamaker常数A131可由式(3)简化为
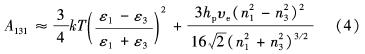
式(4)表明,对于介质中相同物体之间的范德华力总是引力(A>0), 当介质中物体不同时,范德华力可能是引力也可能为斥力,在真空或空气中的凝聚相物体间的范德华力总是引力.在原油-水-岩石体系中,由于地层水通常是具有一定矿化度,具有较高介电常数, 因此, 范德华力通常表现为引力.
经典的DLVO理论已被广泛应用于描述水介质中的各种表面间相互作用,其中包括双电层和范德华相互作用.DLVO力作为分离距离的函数(表1),可以是引力,也可以是斥力,这取决于表面性质和溶液条件.在低渗、特低渗储层中,油相与岩石间范德华和双电层合力应为弱引力或斥力,如果只考虑这两种力,注水开发过程中油膜应易被剥离,但实际水驱油膜剥离效率低下,此现象说明油与岩石间存在非DLVO相互作用,使二者黏附力较大,洗油效率未达预期.
近年来,胶体与界面科学领域的研究在纳米力学技术的推动下取得了长足进步[23-29].文献[43- 45]定量表征了纳米颗粒间范德华力及双电层力,揭示了溶液中纳米颗粒的失稳团聚机制,推动纳米流体的发展,明确了阳离子-π和阴离子-π作用机制及强度,剖析了自修复或自生长凝胶体系界面黏附/黏聚机理.此外 利用纳米力学技术发现水环境中疏水界面间除上述作用力外还存在一种难以由经典DLVO胶化理论解释的疏水相互作用(疏水引力)[46].
在水溶液中,特定分子和基团彼此间有强烈排斥的倾向,这与疏水基团在水溶液中表现的强吸引力相反[20].图6显示了水在亲/疏水表面上的结构,在一个带负电的亲水表面(图6(a)),水分子由于静电相互作用和氢键作用会被强制排列,使水分子中的一个H+指向亲水表面.因此,被取向性地束缚在亲水表面的水分子产生额外的空间壁垒,增加了排斥力.
而疏水表面不具备与水形成氢键的能力,水分子在疏水表面垂直于界面取向(图6(b)),形成有序重排,从而导致体系熵降低,增加系统自由能,这从热力学角度来看是不利的.因此,疏水表面在熵的驱动下,具有减小疏水表面与水的接触面积的趋势,界面间表现出较强的吸引力[46].
图6 界面水结构示意图[20]
Fig.6 Schematic diagram of interface water structure[20]
疏水引力量化测量可以追溯到1982年.ISRAELACHVILI等[47]使用SFA首次直接测量了水溶液中两个疏水表面之间远强于范德华相互作用的远程吸引力,建立疏水表面间疏水引力F与距离D间函数关系F∝exp(-D/D0)(D0为特征衰减长度),指出疏水相互作用的有效作用范围达几十甚至几百nm,并随表面的疏水程度的增加和D0增长而增强.此后,利用SFA和AFM这两种纳米力学实验技术,研究者不断探索和量化各种疏水表面之间的相互作用力以及所涉及的疏水相互作用,取得了很多重要进展[48-51].
疏水引力的大小与两个相互作用表面的黏附力密切相关,在非均匀分布的疏水表面,较大的黏附力代表相对疏水的结构域,而较小的黏附力则表示相对亲水的结构域.XIE等[52]通过— CH3修饰的探针测量化学试剂吸附前后的闪锌矿(ZnS)晶体表面黏附分布图,探讨了其表面疏水性的纳米级非均质性.— CH3修饰的探针也被用于研究石墨烯的厚度对其疏水性的影响,MUNZ等[53]发现在双层石墨烯表面测得的黏附力强于单层石墨烯,表明双层石墨烯比单层石墨烯疏水性更强,这用传统的接触角法是难以测量的,这为量化非均质性较强的储层岩石表面微观润湿性提供可能.
与不可变形系统的力学测量结果相比,可变形系统中疏水引力的测量结果通常与形变和水动力学相关,形变和水动力学的存在使力分离距离的测定和疏水相互作用的精确量化变得困难.气泡-液滴探针技术使可变形物体(如气泡和油滴)的力学测量成为可能,而斯托克-雷诺-杨-拉普拉斯模型可以解释测得的力结果,并计算相互作用表面之间的分离距离[54-55].也有研究利用气泡探针技术定量测量了不同材料中的疏水相互作用,包括聚合物[56]、超疏水表面[57]、沥青[28]和矿物等[58- 60].
尽管对疏水引力的起源、性质以及定量表征研究仍然存在不足,但人们越来越认识到疏水效应是与界面水结构效应密切相关的熵驱动过程[61].不同尺寸的非极性分子会导致水分子氢键网络和结构熵的变化,可变形的空气-水系统和油-水界面疏水引力的衰减长度远小于固体-水系统,表明可以通过改变有序晶体状态和无序液体状态之间的分子排布来调节疏水引力.图7为类晶、非晶和液体表面疏水相互作用的典型力曲线.其中, D0是用于评估疏水引力范围的关键参数,在不同表面具有显著差距.对于类晶体自组装单分子膜表面D0约为1.60 nm; 对于非晶态表面D0为0.75~1.25 nm; 对于纯液体表面D0低至0.30 nm.不同表面D0的显著转变表明疏水相互作用与物质表面特性密切相关.
图7 类晶、非晶和液体表面疏水相互作用的典型力曲线[22]
Fig.7 Typical force curves of hydrophobic interaction for different surfaces[22]
图7 类晶、非晶和液体表面疏水相互作用的典型力曲线[22]
Fig.7 Typical force curves of hydrophobic interaction for different surfaces[22]
文献[28,62- 63]利用AFM液滴探针技术,研究了原油与不同润湿性表面间相互作用,发现原油与疏水表面间存在疏水引力,随着表面疏水程度的增加,疏水引力逐渐增强,当疏水引力克服双电层斥力及空间位阻作用后,油滴将在固体表面吸附铺展.LU等[61,64]研究发现,地层水作为油-固相互作用的环境介质,其物化性质尤其是离子种类及浓度将影响疏水引力微观力学特性.地层水中高价阳离子水合作用及离子-疏水表面特异性相互作用,影响界面处水分子的排布特征,从而影响疏水表面间相互作用力.LIU等[28]通过AFM疏水胶体探针研究发现,油滴与砂岩间也可能存在疏水引力.虽然砂岩整体表现为弱亲水,但胶质、沥青质的黏附及裸露的疏水矿物导致砂岩表面分布着疏水微区[28,63],可能导致油膜壁面黏附.然而,目前关于砂岩表面疏水微区分布及强度尚未形成定量化评价方法,疏水微区如何影响原油-砂岩间疏水作用仍需进一步研究.
文献[31-34, 65-72]研究发现,当地层水中二价阳离子浓度较高时,负电性的亲水表面也存在油膜铺展的现象,意味着除范德华力以外,还存在未知强相互作用机制.文献[34-37]研究表明,这可能是由于原油和岩石均带负电,地层水中的二价阳离子充当了油-固界面间的桥梁,将二者桥连起来(图8),形成阳离子桥.
图8 离子桥连作用示意图[34]
Fig.8 Schematic diagram of ion bridging[34]
文献[31-33]研究表明,地层水的中二价阳离子能够起到桥梁作用,连接原油中带负电的酸性物质与带负电性的砂岩表面,导致油膜铺展.ALSHALABI 等[71]提出地层水中存在的高价阳离子(如Mg2+和Ca2+)水合后可同时与两个甚至多个带负电基团结合,形成离子桥连结构,增强了油膜与岩石间的引力,导致油膜难剥离.文献[34]通过分子动力学模拟,考察了地层水中Ca2+对油-石英间相互作用力的影响.结果表明,随着Ca2+浓度的升高,石英表面Ca2+吸附量增大,表面电势下降.油与岩石靠近过程中酸性组分在油滴表面发生重排,油滴与岩石表面Ca2+引力增大,并最终在石英表面铺展(图9).目前,对于阳离子桥连结构,有两种不同模型,一种认为Ca2+与原油表面负电活性物质(羧酸和磺酸)及岩石表面负电基团直接进行桥连; 另一种认为Ca2+及负电基团先形成水合离子,水合Ca2+通过氢键及静电作用连接原油及岩石表面的水合阴离子,原油-岩石间存在纳米级水膜.可见,对于原油-岩石间阳离子桥的形成机制及作用强度尚缺乏统一、清晰的认识,需进一步深入研究.
除了疏水相互作用和离子桥连作用外,油-水-固界面还存在空间位阻和水化作用等相互作用,也会显著影响洗油效率,一般均称为非DLVO相互作用.例如,储层中存在的黏土或不带电表面活性剂在水溶液中能够自然发生膨胀甚至相互排斥,纳米二氧化硅或其他胶体颗粒在高浓度盐溶液中能保持稳定,这些排斥力就是水化作用[20,75-76].在低渗储层中,水化作用会导致储层黏土膨胀堵塞本就细小的孔喉,对采收率造成不利影响.当聚合物存在于固液界面时,由于两个表面不断接近,覆盖在固液界面的聚合物链会发生重叠压缩,不利于熵增,从而产生排斥性的相互作用力,这被称为空间位阻[20].近年来,纳米材料作为新的3次采油用剂受到越来越广泛的关注,纳米颗粒对微纳尺度油-水-岩石间相互作用的影响不容忽视,比如WASAN 等[73-74]最先发现,当溶液中含有纳米颗粒时,在结构分离压力的作用下,在亲水固体表面将形成一系列不同的纳米颗粒层; KIRTI等[77-78]研究表明,纳米流体在结构分离压力的驱动下能在油滴与固体表面之间形成连续的楔形纳米流体薄膜.此时,油滴、固体表面和纳米流体相交处具有内、外两个三相接触线.通过增加纳米流体的浓度、减小纳米流体的尺寸或者减小界面张力,可以使内接触线自发地运动,从而提高油膜剥离效率.NIKOLOV 等[79]用高倍显微镜研究了油滴、固体表面和纳米流体相交处三相接触线的变化,发现由小液滴(毛细管压力高)形成的膜比由大液滴(毛细管压力低)形成的膜更厚,包含更多的颗粒层,对油滴剥离的效果更明显.但纳米颗粒剥离油膜过程对油膜初始状态较为敏感,当油膜初始接触角小于30°时,楔形结构不易形成,导致油膜剥离效果不理想,驱替后波及区域内仍存在较多残余油.此外,纳米颗粒存在分散难,以及在微纳孔隙中易聚集等问题.可见,纳米颗粒油膜-岩石间强相互作用有一定破坏作用,但破坏作用有限,对纳米颗粒油腊-岩石间强相互作用的机理还需进行深入探索.
对石油开采过程中油-水-岩石微观界面作用机制的全面理解可以为低渗、特低渗油藏的开发工艺的更新及先进功能材料的研制提供重要依据.原油与岩石间相互作用的研究经历了预测-模拟-精准测量的过程.定量解析原油-岩石间相互作用,揭示界面微观构象与作用力间内在联系,阐明油膜岩壁黏附机理,不仅是当前学术研究的热点和难点,也可为高效剥离油膜提供理论支撑,指导驱油材料的设计与研发,对砂岩油藏高效开发具有重要意义.
虽然目前对原油与岩石间相互作用的研究已取得了一定进展,但有几个关键问题需进一步探究.例如,原油-岩石间强相互作用力的形成机制及强度尚未明晰、物理化学原理尚未阐明; 地层水中离子种类、浓度及岩石表面微观润湿性对作用力强度的影响尚未明确.因此,需进一步通过纳米力学技术定量解析原油-岩石间相互作用力并建立数学模型,研究动静态条件下原油-岩石界面分子排布特征,揭示界面微观构象与作用力间内在联系,阐明油膜岩壁黏附机理.此外,需研究残余油分布规律及滞留状态,建立原油-岩石间相互作用与残余油膜赋存状态间映射关系.这将为提高砂岩油田采收率提供理论支撑,同时还将丰富和发展胶体与界面科学,具有重要的实际应用及学术价值.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N