作者简介:胡歆迪(1996—),南京医科大学硕士研究生.研究方向:医学图像处理.E-mail:h15851832081@163.com
中文责编:英 子; 英文责编:木 柯
1)南京医科大学生物医生工程与信息学院,江苏南京211166; 2)深圳大学医学部生物医学工程学院,广东深圳 518060; 3)广东省妇幼保健院超声诊断科,广东广州511400
1)School of Biomedical Engineering and Information, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, Jiangsu Province, P.R.China;2)School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University, Health Science Center, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, P.R.China;3)Ultrasound Department, Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, P.R.China
artificial intelligence; developmental dysplasia of the hip; standard plane; image classification; instance segmentation; computer aided diagnosis; deep learning; feature extraction
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.04408
髋关节发育性不良(developmental dysplasia of the hip, DDH)是一种常见的先天性关节疾病,发病率为0.15%~2.00%[1].该疾病由股骨头和髋臼之间位置异常引起,患病婴儿髋臼较浅,股骨头无法牢固地嵌在髋臼内,甚至完全脱出髋臼.根据病情严重程度,DDH可分为发育不良、半脱位和脱位3类.常见的临床症状包括左右腿长度不等,腿纹和臀纹不对称,脱位腿向外翻转等,不及时治疗可能会引发慢性疼痛、步态紊乱和关节炎等疾病[2].DDH早期的治疗简单有效,治疗成功率可达96%[3],能有效减少后续疾病的产生,因此针对新生儿的DDH筛查具有重要意义.与X光相比,超声成像具有无创和无辐射等特点,且能显示婴儿髋关节尚未骨化的部分,便于观察股骨头在髋臼内的运动,因此对6月龄以内的婴儿,临床上通常使用超声检查,依据Graf法进行DDH诊断.
Graf法是一种基于形态学的方法,通过量化解剖结构在超声静态图像上的特征,评估髋关节发育状况[4].Graf法通常分为3步:① 使用超声探头扫查婴儿髋关节(图1(a)),获得超声视频.② 从超声视频中挑选出一张标准切面图,该图必须包含平直髂骨、髂骨下缘、盂唇和骨-软骨结合处等关键解剖结构,如图1(b).由于平直髂骨和髂骨下缘同属于髂骨结构,为便于测量角度,本研究将二者视作不同结构.③ 在标准切面上测量α角和β角两个发育指标.如图1(c)和(d),角度测量需要作出3条测量线:沿平直髂骨顶部作出切线,即基线; 从髂骨最下缘点向平直髂骨外轮廓作出切线,即骨顶线; 连接盂唇中心点和平直软骨下端点,即软骨顶线. α角为基线和骨顶线的夹角, β角为基线和软骨顶线的夹角.④ 结合婴儿年龄等信息,对髋关节进行分型.
尽管Graf法已在临床上得到了广泛应用,但其主观依赖性较强,整个筛查流程耗时费力.在实际应用中面临如下难点:① 标准切面获取困难,易出现误判和漏判.一方面,在进行超声筛查时,婴儿易动,增加了扫查到标准切面的难度; 另一方面,标准切面的判断标准严格,对医生的专业知识和临床经验要求较高.② 参数测量主观依赖性强.由于超声图像存在噪声和伪影等问题,质量较差,且医生对解剖结构的形态判断依赖自身经验,造成不同观察者之间的测量结果差异较大,即使是经验丰富的医生, α角和β角的测量差异也能达到3°和6°[5],尤其在基层医院,医生临床经验匮乏等问题更为突出.因此,亟需一种规范且高效化的方法进行超声DDH筛查.
近年来,计算机辅助诊断(computer aided diagnosis, CAD)超声筛查DDH的相关技术不断出现,但均存在一定局限性.首先,标准切面的重要性常被忽视,辅助识别DDH标准切面的技术尚无人研究.标准切面是精准化超声检查的前提,唯有在标准切面上对发育指标进行测量,才能保证数据的准确性和可靠性.虽然自动识别标准切面在多个超声筛查项目中都得到了重视[6-8],但由于标注数据需求量大且切面识别难度高等问题,在DDH超声筛查方向鲜有进展.其次,现有的参数测量相关的CAD技术,速度和精度都难以满足实际临床需求.这些技术通常是基于关键解剖结构的轮廓特征来计算α角和β角.根据特征提取的方法,该技术可分为基于手工提取特征的传统方法和基于深度学习的人工智能方法.传统方法如使用测地线动态区域(geodesic active regions, GAR)[3]和相位对称性[9]等方法提取图像特征,往往受限于手工特征提取的复杂度,模型精度低且鲁棒性差.由于深度学习可自动提取图像特征,善于解决大量数据中的高维难题,在髋关节超声图像分析领域也得到了初步应用.例如,经典的全卷积网络(full convolution network,FCN)[10]和Unet[11]等,被用于分割髂骨或盂唇的任务[12-13]; 使用对抗学习的卷积神经网络分割平直髂骨和髂骨下缘[14]; 多尺度的特征融合网络用于获得骨结构的概率图[15].但现有的辅助DDH超声筛查方法仍存在两个缺陷:① 仅聚焦于局部解剖结构的轮廓信息,缺少对重要解剖结构的标识.Graf法的准确度非常依赖医生对解剖结构的识别,这对缺乏经验的医生来说存在一定困难,自动化的结构标识能够为医生提供示教帮助,有利于初学医生快速上手、加深对DDH超声筛查的理解.② 推理速度较慢,实际应用受限.
进一步推动自动化超声筛查DDH的发展,需要解决以下问题:① 对于常用于识别标准切面的分类神经网络,其准确率越高,所需训练样本量越大,但训练数据的获取和标注都会消耗大量时间和人力成本.视频数据的标注更是耗时耗力,逐帧标注会给医生带来沉重的工作负担,数据集规模也因此受到限制.② 对于髋关节结构的分割任务,由于超声图像质量较差,常出现结构边缘模糊和结构黏连等问题,导致分割精度差; 髋关节结构复杂,结构之间超声成像辨识度低,易造成误分割.③ 实际诊断中,需要实时测量或多次测量,对模型的推理速度有较高要求.
本研究提出一种智能化DDH辅助筛查系统,由标准切面自动识别模块和发育参数自动测量模块构成.自动识别标准切面模块依赖一个基于少样本单类别分类(few-shot one-class classifier, FOC)的神经网络,该网络有两个优势:① 基于少样本:仅需1/3训练样本训练模型,大幅减少医生的标注工作量; ② 基于单类别,即仅使用标准切面图像训练网络,可强化网络对标准切面的学习程度.自动测量模块依赖一个能够自动测量的快速实例网络(fast instance network, FIN),该网络优势为:① 可以提供关键解剖结构的标识,为医生起到示教作用; ② 目标定位功能大幅减少了误分割的发生概率,多任务模型提高了分割的精度; ③ 推理速度超过30帧/s,为临床筛查节省时间,提高了效率.该系统首次将标准切面的判断融入自动诊断过程,实现质量控制,提高同质化水平,同时优化工作流,加快了工作效率,提高了测量准确度.
本研究提出的智能化DDH辅助筛查系统的架构如图2.医生使用超声探头扫查婴儿髋关节获得视频数据并输入标准切面自动识别模块; 已被判定为标准切面的图像被送入自动测量模块,该模块会自动检测和分割出关键解剖结构(平直髂骨、髂骨下缘、盂唇和骨-软骨结合处),并自动测量出α角和β角,最后将结果展示在图像中以供参考.
本研究提出的FOC分类神经网络,仅需少量阳性样本,即标准切面,作为学习对象,通过自监督训练方式学习标准切面的特征信息,从而为未知图像打出标准化评分.该方法可大幅减少对训练数据和人工标注数量的依赖.
自动识别标准切面可视为图像二分类任务,需要将输入图像归类至标准切面或非标准切面,但在婴儿髋关节的超声视频中,训练二分类网络存在一定的挑战:① 二分类网络同时需要阳性和阴性样本,标准切面有明确定义,即至少包含平直髂骨、髂骨下缘、盂唇和骨-软骨结合处4个解剖结构(见图1(b)),不满足此定义的图像,如解剖结构显示不全、 噪声图等, 均为非标准切面. 但通常情况下,难以获得所有种类的非标准切面.② 超声图像质量较差,因此分类难度大,且高精度的网络模型需要大量数据进行训练,数据采集和标注工作量大.
作为一种特殊的分类任务,单分类任务只需判断未知样本是否为目标类,无需判定非目标类样本类别.该任务适用于正负训练样本极度不均衡的任务,如训练样本全部为正样本、大量正样本和极少数的负样本、大量正样本和无数类难以标注的负样本等[16].常见的单分类模型可分为:① 基于分类的方法,如基于支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)的单类别支持向量机(one-class support vector machine, OCSVM)[17]和深度支持向量数据描述(deep support vector data description, deep SVDD)[18]; ② 基于无监督或自监督的几何变换网络(geometric transformations, GEOM)[19]和自监督的分布外检测(self-supervised out of distribution, SSOOD)[20]等; ③ 基于图像重建的变分自编码器(variational auto-encoder, VAE)[21]和对抗生成网络Ganomaly[22]等; ④ 基于数据分布建模的深度自动编码高斯混合模型[23]等.因此,可仅使用标准切面训练一个单分类网络.该网络仅需充分学习标准切面的图像特征分布,并判定所有不符合该单类特征分布的图像为非标准切面,以此实现超声视频中标准切面的自动化识别.
由于DDH标准切面的标注数据量少,对单分类网络的训练造成一定困难.因此,本研究引入自监督学习策略.与全监督学习相比,采用自监督学习训练神经网络成本低且效率高.自监督学习通过特定方式为训练数据生成伪标签,并用该标签辅助下游任务.该方法适用于无标注或稀缺标注的数据集.自监督学习在单分类任务中也得到了成功应用,例如GEOM和SSOOD等.对于DDH标准切面识别的任务,在数据集仅有少量标准切面的情况下,可通过自监督的方式对数据集进行拓展,使网络学习到标准切面的深度特征.
标准切面自动识别网络由几何变换模块和监督学习模块构成,如图3.网络训练时,首先将髋关节标准切面图像x送入几何变换模块进行数据扩增,并生成伪标签; 扩增后的图像和伪标签被送入监督学习模块进行特征学习.几何变换T由3步操作构成:① 水平平移TH, TH={TH0, TH1, TH2}. 其中, TH0、 TH1和TH2分别表示将图像在水平方向上平移0、 +n或-n个像素.② 垂直平移TV, TV={TV0, TV1, TV2}. 其中, TV0、 TV1和TV2分别将图像在垂直方向上平移0、 +n或-n个像素.③ 旋转TR, TR={T0, T1, T2, T3}. 其中, T0、 T1、 T2和T3分别将图像旋转0°、90°、180°和270°.在数据扩增过程中,图像在水平和垂直方向各取一个数值进行平移变换,随后分别旋转4个角度,即每张图像先进行9种组合平移操作,再分别进行4种旋转变换,共经历36种几何变换组合.几何变换模块为每张变换后的图像生成一个大小为1×3的标签矩阵,该矩阵由水平平移操作(TH={TH0, TH1, TH2})的标签h(h∈H={0, 1, 2}, 垂直平移操作(TV={TV0, TV1, TV2})的标签v(v∈V={0, 1, 2})和旋转操作(TR={T0, T1, T2, T3})的标签r(r∈R={0, 1, 2, 3})拼接而成.变换后的图像和伪标签一起被送入特征提取网络并进行监督学习.
本实验使用Resnet34[24]作为特征提取网络,提取的图像特征分别送入3个softmax层进行标签预测,则由预测标签与自监督标签得到的损失函数为
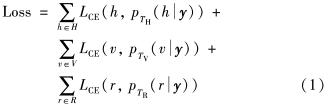
其中, LCE为交叉熵损失函数; pt(t|y)(t∈{TH, TV, TR})表示网络对操作t的softmax预测值; y=T(x)为经过几何变换模块后的图像.
预测时,输入一张未知图像,经过几何变换后送入监督学习模块.网络预测图像的3种变换的标签值,并计算出标准置信度为
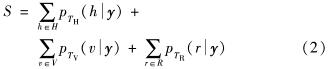
由式(2)可见,若输入的图像越标准,网络预测的几何变换组合越准确, S值越大.最后手动定义一个分类的阈值t, 若S>t, 则该图最终预测为标准切面; 反之,则为非标准切面.找到验证集分类性能最好的分类阈值,作为该网络的最佳阈值.
自动识别标准切面模块输出的标准切面图,进入自动测量模块.为实现自动测量α角和β角功能,需获取3条测量线,而这些测量线又依赖于关键解剖结构的轮廓(图1(d)),因此,该模块首先需要提取出髂骨、髂骨下缘和盂唇的轮廓线.通常使用分割网络提取关键结构的语义信息,再计算出轮廓线.该过程存在两个困难:① 由于超声图像质量较差、结构边缘辨模糊,不同结构间辨识度低,语义分割网络的精度难以得到保证; ② 大型网络的推理速度较慢,难以达到实时辅助筛查的速度.
与语义分割任务不同,实例分割对每一个目标同时预测位置和轮廓信息.引入位置信息可以辅助提升分割精度,并有效改善误分割问题.实例分割网络分为双阶段模式和单阶段模式.双阶段模式如mask R-CNN[25],需要先对目标区域检测,再对检测区域内部结构进行分割,两阶段串行进行,计算效率低.单阶段实例分割网络如Yolact[26]等,舍弃了耗时的区域定位操作,因此尽管牺牲了少量精度,但大幅提高了推理速度.
本研究提出一种能够自动测量的快速实例分割网络FIN,结构如图4.由图4可见,髋关节图像需先经过特征提取模块,提取出图像特征再分别送入原型掩膜生成模块和预测模块.前者用于生成固定数量的原型掩膜,后者用于生成原型掩膜的系数,二者结合可计算出最终的分割结果,并基于此结果出测量α角和β角.
1)特征提取网络使用特征金字塔网络(feature pyramid network, FPN)[27]作为骨干结构.卷积神经网络随着网络深度的增加,生成的特征图(C1~C5)空间分辨率逐渐变小,形成金字塔结构.浅层的网络输出高分辨率特征图,包含大量纹理特征和少量语义特征; 深层的网络输出低分辨率特征图,包含少量纹理特征和大量语义特征.FPN将自下而上和自上而下的两个金字塔网络横向连接在一起,因此每层输出的特征图(P3~P7)融合了不同尺度的纹理特征和语义特征,有效提升了精度.在本实验中,骨干网络采用Resnet50-FPN网络结构.
2)原型掩膜生成模块使用FCN结构,输入FPN的特征图 P3,经过若干3×3卷积和一个1×1卷积操作后,输出尺寸为138×138×k像素的原型掩膜.其中, k为原型掩膜的个数; 138×138为一个原型掩膜的图像分辨率.
3)预测模块输入5张特征图 P3~P7, 预先定义对每个像素点生成固定长宽比的3个锚框,因此对于一张分辨率为Wi×Hi的特征图 Pi(i为特征图序号, i=3, 4,…, 7,), 共生成Wi×Hi×3个锚框,其中每个锚框需要3种类型的预测结果:类别置信度、边界框偏移量和掩膜系数.
特征图 Pi经过2个3×3卷积层后,得到尺寸为Wi×Hi×256的特征图.随后分别进入3个平行的预测分支:一个用于分类预测,输出c个类别的
置信度; 一个用于回归边界框的4个偏移量; 一个用于掩膜系数预测,对于k个原型掩膜,该分支也将输出k个系数.因此,对于特征图 Pi, 该模块共输出ai=(c+4+k)×Wi×Hi×3个预测值.最后,将所有特征图的预测结果进行拼接,得到所有锚框的预测值.
通过预测模块获得候选框的集合,由于框体之间存在大量重叠,还需进行筛选才能获得最合适的检测框结果,此操作被称为非极大值抑制(non-maximum suppression, NMS).传统的NMS方法顺序计算所有框之间的重叠程度,耗时巨大.为加快推理速度,FIN使用快速NMS方法[26],通过并行计算进行加速.首先,网络输出c个类别的n个检测框,对于每个类别, n个检测框按类别得分降序排列,生成一个大小为n×n的矩阵; 计算该矩阵与自身的交并比(intersection over union, IoU),获得IoU矩阵X; 对X进行上三角化,得到X'; 对X'按列取最大值,并与NMS阈值进行比较,保留小于阈值的候选框,即为最后的检测框.
预测模块输出的掩膜系数和原型掩膜,可通过线性组合生成预测的掩膜,即
M=σ(PCT)(3)
其中, P为大小为Wi×Hi×k的原型掩膜矩阵; C为大小为m×k的掩膜系数矩阵, m为实例个数; σ(·)为sigmoid函数.计算得到的掩膜经过检测框裁剪,只保留边框内部的掩膜为最终预测掩膜.
该网络的损失函数为
L=Lcls+Lbox+Lmask(4)
其中, Lcls为分类损失函数; Lbox为检测损失函数,二者详细计算方式可见单阶段多目标检测网络(single shot multibox detector, SSD)[28],掩膜预测的损失函数Lmask为预测掩膜 M和金标准(ground truth, GT)掩膜MGT之间的二进制交叉熵(binary cross entropy, BCE),即Lmask=BCE(M, MGT).
除了3个测量所需的解剖结构,本研究额外增加了骨-软骨结合处的实例分割,因为该结构为标准切面的必备结构之一,将其展示在图像上有助于医生辨识、强化理解标准切面的特征.
本研究共采集634例婴儿髋关节超声数据,每例包含左右两侧髋关节的标准切面图,其中185例包含髋关节超声视频.所有数据采集自广东省妇幼保健院超声科,超声设备的型号为日立HIVSON,详细数据分布如表1.其中,用于标准切面分类实验的185个病例包含329个超声视频,每个视频均由高年资医生(临床经验10年及以上)逐帧标注出是否为标准切面.用于自动测量实验的634个病例,包含1 321张超声标准切面图像,每个病例包含左右两侧髋关节图像,每张图均由高年资医生标注出4个关键解剖结构(髂骨、髂骨下缘、盂唇和骨-软骨结合处)的轮廓.
实验将该网络和常见的单分类网络进行对比.训练时仅使用约30%的标准切面,且不使用非标准切面,数据集划分如表2.所有图像统一缩放至224×224像素,且经过图像标准化的处理,即图像像素矩阵减去其均值并除以其标准差.
实验使用的单分类网络有:① OCSVM.由于方向梯度直方图(histogram of oriented gradient, HOG)能够有效提取超声图像的特征[29],因此先用该方法提取髋关节图像的63 504维特征,再使用SVM学习特征向量并进行分类.② deep SVDD[18].基于单类别SVM的思想,使用神经网络拟合出一个包裹所有标准切面特征的超球体,通过最小化超球面的半径来迭代优化网络模型.推理时,该模型将未知图像映射到特征空间,可计算出该图像特征与超球体的位置关系.若该样本在球体内部,则认为该图像为标准切面; 反之,则为非标准切面.实验使用Resnet34作为特征提取的主干网络,并丢弃最后的分类层,以特征空间原点为球心建立超球体模型,提取512维图像特征计算超球体的半径.③ Ganomaly[22].该方法基于两个一致性原理,即重建图与原图一致、重建图的编码与原图的编码一致,构造出编码-解码-编码的网络结构,并融入对抗训练的思想,使网络同时学习到训练样本的图像特征和隐空间特征.④ FOC.使用pytorch学习框架,学习率为5×10-4,优化器为随机梯度下降法(stochastic gradient descent, SGD),共迭代100个epoch.操作系统为Linux,使用两块GPU进行训练,型号为NVIDIA GTX 2080Ti.
单分类网络输出为图像的标准置信度,无法根据训练集确定合适的分类阈值,因此实验使用需要包含标准切面和非标准切面的验证集的辅助验证,选取最优模型.上述实验均使用五折交叉验证.
分类网络的评估指标包含接受者操作特征曲线下面积(area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, AUROC)、平均精度(average precision, AP)、FPR95、准确率(accuracy, ACC)、精确率(precision)、召回率(recall)和F1值.其中,FPR95为常见的单分类性能评估指标之一,表示TPR为95%时FPR的值,即阳性样本中的95%被正确分类时,阴性样本中被误分类为阳性的比例,其值越小越好.在得到标准置信度的ROC曲线后,通过约登指数计算出最佳分类阈值,置信度高于此阈值,则认为该图为标准切面; 反之,则为非标准.根据分类结果,可计算出ACC、precision、recall和F1值.
表4为不同分类网络性能的定量评估结果.由表4可见,FOC网络的所有指标均优于其他单分类网络.图5为不同分类网络的AUROC曲线的对比.由图5可见,FOC网络的曲线高于其他网络,说明在仅使用少量样本的情况下,其分类性能明显优于其他单分类网络.原因在于几何变换的组合扩增了训练样本量; 监督网络识别几何变换,可以促使网络学习到标准切面的关键特征.
临床上DDH超声筛查更看重视频中的标准切面能被正确识别的比例,即recall值越高越好.由表4可见,FOC网络的recall值明显高于其他分类器,表明其实用价值更高.但是,FOC网络对非标准切面的识别能力较差,易将非标准切面误判为标准切面,尤其是在识别一些接近标准但非标准的切面图像时.如图6(b)的非标准切面,髂骨下缘不够清晰,但整体形态非常接近标准切面,由于FOC网络没有学习过此类负样本的图像特征,处理细微结构差异的能力较差,因此将其误判为标准切面.
表4 不同单分类网络性能的定量评估结果1),2)
Table 4 Quantitative evaluation results of different classification networks%
图5 不同分类网络ROC曲线对比
Fig.5 Comparison of receiver operating characteristic curve of different classification networks
本实验将提出的自动测量网络与常用的语义分割网络对比.由于语义分割网络只输出分割结果,为保证结果一致性,使用分割结果生成最小外接框并计算检测相关的指标.所有网络输入图像大小均设为512×512像素,且经过旋转、平移、缩放和亮度变换等数据增强操作.
进行对比实验的网络包括:① FCN:先使用卷积网络提取图像特征,再通过反卷积将特征图恢复到原图大小,最后对每一个像素生成一个类别标签,从而实现语义分割.本实验中使用VGG16作为FCN的特征提取网络.② Unet:该网络通过跳跃连接,将不同尺度的特征图依次融合入上采样的过程,使网络有效学习到多尺度的特征,提高了分割精度,已在医学图像领域得到广泛应用.③ deeplab V3[30]:基于Resnet网络结构的多重网格操作和改进的空洞金字塔池化操作,能有效提取多尺度的图像特征信息.在本实验中使用Resnet34作为骨干网络.④ FIN:使用pytorch学习框架,学习率为1×10-4,优化器为SGD,共迭代150个epoch.操作系统为Linux,使用一块型号为NVIDIA GTX 2080Ti的GPU进行训练.上述实验均使用五折交叉验证.
1)检测指标:① 平均交并比(mean intersection over union, mIoU),即所有类别预测框与真实框之间IoU的均值,反应了检测框与真实框之间的相似度,该值越大越好; ② 平均精度均值(mean average precision, mAP),即所有类别的平均精度的均值.手动设定一个阈值,当IoU大于该阈值,则认为该预测框预测正确,反之则错误.设置不同阈值,可以计算不同的precision和recall值,并计算出平均精度.mAP值越大越好.
2)分割指标:① Dice相似性系数(Dice similarity coefficient, DSC)用于评估两个分割区域X和Y的相似性,即
DSC(X, Y)=(2(X∩Y))/(X+Y)(5)
在本研究中, DSC(X, Y)用于计算网络分割结果和标注结果的相似度,其值越大相似度越高; ② Jaccard系数(Jaccard coefficient, JAC)用于衡量两个分割区域X和Y之间的相似性,即
JAC(X, Y)=(2(X∩Y))/(X∪Y)(6)
JAC值越大表明两个区间相似度越高; ③ Hausdorff距离(Hausdorff distance, HD)用于描述两个分割区域X和Y边缘之间的距离,即
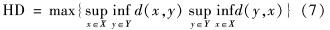
其中, x和y分别区域X和Y中的点; d(x,y)表示点x和点y之间的欧氏距离; sup代表上确界; inf代表下确界.HD值越小越好; ④平均表面距离(average surface distance, ASD)表示分割结果X的所有的到表面距离的平均值,即
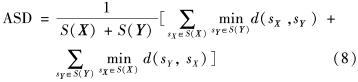
其中, S(X)和S(Y)分别表示分割区域 X和Y的边缘线,sX和sY为X和Y的边缘点; d(sX, sY)为sX和sY的欧式距离.ASD值越小越好.
3)测量指标:采用平均绝对误差(mean absolute error, MAD)计算预测角度与标准角度之间的绝对误差,该值越小表示角度预测越准确.
4)推理速度:采用每秒处理帧数(frames per second, FPS)反应网络推理的速度.为保证结果公正,本实验中的时间计算考虑到网络推理和自动测量,且不同网络的测量操作相同.
此外,在计算检测和分割指标时去除了背景类,以防大面积的背景对结果可靠性造成影响.
表5为不同网络的目标检测和分割性能.由表5可见,FIN网络的所有指标都优于其他网络,其中mIoU和mAP值高说明该网络对解剖结构的定位更精准; DSC和JAC指标高说明该网络对解剖结构的分割更准确; HD和ASD值低说明该网络在结构轮廓上的分割更好; FPS=33.88帧/s,符合实时测量的要求.虽然FCN的FPS也超过了30帧/s,但它们在分割与检测的任务上表现欠佳.可见,单阶段的实例分割网络架构和快速NMS方法能够有效使FIN兼顾了速度与精准度,综合性能优于其他分割网络.
表5 不同网络目标检测及分割性能的定量评估结果1)2)
Table 5 Quantitative evaluation results of object detection and segmentation performance of different networks
图7为不同网络分割结果的定性展示,限于篇幅,更多定性对比分割结果图请扫描论文页末右下角二维码查看补充材料图S1.其中,图7(a)为医生标注的标准图; 图7(b)—(d)为不同语义分割网络输出结果; 图7(e)为FIN的分割结果.由图7可见,语义分割网络的输出结果会出现分割缺失的现象,如盂唇分割不全(图7(c)红色区域)和骨软骨结合处分割不全(图7(d)紫色区域)等; 也会出现误分割的现象,将其他结构识别为目标结构(图7(b)绿色区域、图7(d)绿色和紫色区域)等.补充材料图S1从更多方面展示了语义分割的误差,例如平直髂骨误分割为髂骨下缘(第1行第2第3列绿色区域)、骨软骨交界处误分割为平直髂骨(第2行第3列蓝色区域)等.上述分割的误差不仅影响结构的标识,也会影响角度测量的精度.与语义分割网络相比,FIN网络明显改善了上述问题,同时在分割的完整性上得到了提升,原因在于多任务的学习模式使得各个任务之间互相促进,同时检测任务可有效过滤了非目标区域的误分割结果.
表6为不同网络自动测角的MAD性能.其中,FIN网络有着最高的测量精度, α角的MAD为2.48°, β角的MAD为4.38°,二者均为最低.图8可视化了FIN角度测量结果,与标准测量值误差很小.同时,该实验额外统计不同医生间手工测量的误差.对于每一张测试用图,由高年资医生标注出标准数值,再由其他医生独立手动测量一遍,二者的差值即为手工测量误差.由表6可见,FIN网络的角度误差小于手工测量误差,说明该方法可减少不同医生之间的测量差异,辅助临床筛查更标准化和精确化.
表6 不同网络自动测量结果与标准值的MAD1)
Table 6 MAD between automatic measurement results and standard values of different networks
结 语
提出一个智能化DDH辅助诊断系统,读取婴儿髋关节超声视频后,通过FOC网络模块自动识别标准切面,随后将标准切面输入FIN模块,快速测量出α角和β角后,再将可视化测量结果展示于关键解剖结构标识.与其他基准网络OCSVM、deep SVDD和Ganomaly的对比实验结果表明,FOC网络对标准切面的识别存在明显优势.FIN网络在速度和精度上均优于FCN、Unet和deeplab V3网络.该系统对标注数据量的要求较低,可提升DDH临床筛查的同质化水平,控制测量质量,提高临床医生的工作效率.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N