作者简介:于军琪(1969—),西安建筑科技大学教授.研究方向:智能建筑.E-mail:junqiyu@126.com
中文责编:英 子; 英文责编:木 柯
西安建筑科技大学建筑设备科学与工程学院,陕西西安 710055
School of Building Services Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an 710055, Shaanxi Province, P.R.China
computer neural network; affinity propagation(AP); similar day selection; seeker optimization algorithm; radial basis function; electricity consumption of buildings; short-term load forecasting
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.03315
大型公共建筑能耗大约占建筑总能耗的1/3,近年来随着社会经济的发展,该比例越来越大[1],这令大型公共建筑能耗逐渐成为研究焦点.准确可靠的大型公共建筑用电短期负荷预测(short-term load forecasting, STLF)是建筑进行合理能源调度和节能优化运行的前提.与长期预测相比,时效性较高的STLF主要用于供配电的合理规划,受温差和湿度等突变因素影响大,属于动态非线性时间序列[2].
近年来,许多学者提出了如人工神经网络(artificial neural network, ANN)、自回归(auto regressive, AR)、支持向量回归(support vector regression, SVR)及灰色模型(gray model, GM)等预测模型[2- 6].然而,AR模型根据平稳线性特征处理时间序列,难以适应动态非线性的STLF时间序列; SVR更适合小样本数据,在面对大规模训练样本时,收敛速度慢; GM适用于单调变化的时间序列,难以预测波动较大的时间序列[7].针对逆传播(back propagation, BP)神经网络存在收敛速度慢、易陷入局部极小值的不足[8],径向基(radial basis function, RBF)神经网络因只有一个隐层所以具有收敛速度快的特点,被广泛用于不同的实际需求中[9-10].选取合适的网络参数是提高RBF性能的有效手段[11].回立川等[12]采用近邻传播算法获取RBF神经网络的中心矢量,提高了网络的训练精度,但算法收敛速度慢.翟莹莹等[13]通过改进k-means++算法和方差度量法,提出一种组合式的RBF参数优化方法,但该方法仍存在过拟合的问题.
搜索者优化算法(seeker optimization algorithm, SOA)是一种基于人群的启发式搜索算法[14],其全局搜索能力比粒子群优化(particle swarm optimization, PSO)算法强,且不易受局部极值的影响[15].尽管有研究人员成功将SOA用于参数寻优和模型改进中[16-17],但收敛速度慢和搜索精度低的缺陷仍令寻优结果不理想[18].
此外,考虑到气象和时间等因素对建筑用电负荷的影响[19],进行相似日选取可提升负荷预测模型的性能.吸引子传播(affinity propagation, AP)算法通过在待聚类对象之间传递相似度进行聚类[20],与传统的k-means和模糊c均值聚类算法相比,AP算法参数设定简单,所有样本均参与竞争迭代,与目标对象的主要特征匹配更精准[7].因此,本研究采用AP聚类算法分解样本空间,以期更准确的满足天气及日期类型的需求.
为提高利用RBF神经网络对大型公共建筑短期用电负荷预测的精度和速度,提出一种基于融合策略的改进人群搜索算法(fusion improvement seeker optimization algorithm, FISOA),通过对传统SOA算法引入自适应速度因子,加快对RBF网络参数的寻优速度; 采用多人协同搜索策略提高寻优效率; 通过精英后代遗传策略降低解的随机性,并利用FISOA优化RBF神经网络的中心、宽度和权值.仿真实验结果显示,本研究所提基于AP相似日选取与FISOA-RBF神经网络模型(简称AP-FISOA-RBF模型),能有效处理连续非线性动态规划问题,在预测精度和运行速度上均表现良好.
AP作为一种无监督聚类算法,能更快更优地处理大规模数据[21].AP相似日理论的关键在于建立给定历史数据的相似性矩阵,并根据聚类特征获取历史负荷样本数据的相似日聚类结果.利用欧式距离定义任意两个样本Xi与Xj之间的相似度为
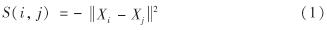
则所有样品的相似度构成相似度矩阵 S.
AP算法通过在待聚类样本数据之间不断迭代代表矩阵R和归属矩阵A,并逐渐收敛至聚类中心[20],每个聚类中心点即该类样本的代表. 第t次迭代时,样本点j适合作为样本点i的聚类中心的代表度Rt(i, j)为
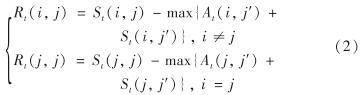
其中, j'≠j, 表示除样本点j以外的其他样本点.因此,加入阻尼调节后实际的代表度Ract(t+1)为第t+1次迭代与第t次迭代的加权和,即
Ract(t+1)=(1-λ)Rt+1+λRt(3)
At(i, j)为第t次迭代时, 样本点i选择样本点j作为聚类中心的合适程度即归属度,表达式为

其中, i'≠i, 表示除样本点i以外的其他样本点. 同样的,加入阻尼调节后实际的归属度 Aact(t+1)的更新规则为
Aact(t+1)=(1-λ)At+1+λAt(5)
其中, i为待聚类中心; λ为阻尼因子, λ∈(0, 1)默认λ=0.75. 决策矩阵为所有样本点的归属度矩阵 A与代表度矩阵 R的和. λ的引入可避免在迭代过程中产生数据振荡,保证决策矩阵的稳定收敛.当矩阵收敛时,将决策矩阵中的对角线元素大于0的数据点作为聚类中心,其余点按照决策矩阵中最大值所在位置依次分配到各个聚类中心[20].
RBF神经网络作为3层反馈神经网络,基本结构包含n个神经元节点的输入层, m个节点的隐含层和k个节点的输出层[12].RBF神经网络利用径向基函数作为单隐层空间的基,能将输入矢量 X=[x1, x2, …, xn]T直接映射到隐层空间,并经隐层快速完成与输出层的线性映射,大大加快了RBF的学习速度并避免算法陷入局部最优,提高了非线性拟合能力,适用于具有复杂非线性特点的建筑用电负荷预测.隐含层 H的第j个节点径向基函数是一个高斯函数,表达式为
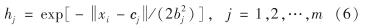
其中, xi为第i个输入样本; cj为第j个网络节点中心; bj为第j个网络节点的网络基宽.网络输出 Y=[y1,y2,…,yk]T中的第k个节点由隐层函数的线性加权和表示,即
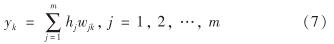
其中,wjk为第j个隐层节点到第k个输出节点的权值.
SOA通过模拟人的智能搜索行为,寻求问题最优解[14].算法以搜索队列为种群,根据智能群体的经验梯度和不确定推理行为,确定搜索方向和步长,进行适应度评价并完成位置更新,逐步逼近问题的最优解,实现问题的全局优化[22].
采用线性隶属函数表示搜索步长模糊变量,结合文献[22],设在最佳位置有最大隶属度值umax=0.900 0, 最差位置有最小隶属度umin=0.011 1. 适应度函数值i的隶属度ui和j维搜索空间适应度函数值i的隶属度ui, j分别为
ui=umax-(s-Ii)/(s-I)(umax-umin), i=1,2,…,s(8)
ui, j=rand(ui,1), j=1,2,…,D(9)
其中, s为种群规模; Ii为种群按适应度降序排列后的个体位置编号, I=1; rand()为随机数产生函数; D为问题维数.
由ui, j得到第j维空间的搜索步长为
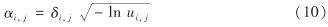
其中, δi, j为高斯隶属度函数参数, δi, j=β|xmin- xmax|; xmin和 xmax是同一种群中最小和最大函数值位置; 惯性权值β跟随迭代过程从0.9线性递减至0.1, β=(tmax-t)/tmax; t和tmax为当前及最大迭代次数.αi, j在每迭代中都不小于0.
第i个搜寻个体的搜索方向 di(t)由利己方向di,ego、利他方向di,alt和预动方向di,pro加权确定[20],即
di(t)=sign(βdi,pro+φ1di,ego+φ2di,alt)(11)
di,ego=pi,best-xi(t)(12)
di,alt=gi,best-xi(t)(13)
di,pro=xi(t1)-xi(t2)(14)
其中, sign()为符号函数; φ1和φ2为[0, 1]内的常数; xi(t1)和xi(t2)分别为{xi(t-2), xi(t-1), xi(t)}中的前2名最佳位置; gi,best为第i个搜寻个体所在种群的集体历史最佳位置; pi,best为第i个搜寻个体到目前为止经历过的最佳位置.
根据搜索方向和步长可实现位置的更新为
xi, j(t+1)=xi, j(t)+Δxi, j(t+1)(15)
其中, Δxi, j(t+1)=ai, j(t)di, j(t); di, j(t)为第j维空间的第i个搜寻个体的搜索方向.
针对传统SOA收敛速度慢的问题,本研究提出的FISOA在搜索过程中,引入自适应搜索速度v及适应系数η, 以实现速度自适应,令SOA的迭代更新速度在数据量较大时,也能保持在良好水平.
第i个搜寻个体在j维空间里的速度适应过程为

其中, t为迭代次数; βmin和βmax分别为惯性权重最小值和最大值; f为当前位置的适应度; fmin和favg分别为适应度最小值和平均值.
传统SOA的单队列搜索模式严重影响搜索的效率和成功率,因此,本研究模拟人类的合作行为,提出一种多人协同搜索模式,通过将全体划分为多个子群体,使得在每一个子群体空间都能同时更新搜索步长、方向和速度,并根据适应度条件判断是否完成搜索.
设s为群体规模, l为每个子群体中的个体数,则子目标群体数g=s/l. 至此,可建立g×l维的解空间矩阵 X=(xij). 其中, i=1, 2, …, g; j=1, 2, …, l.
为提高SOA解空间的质量,本研究提出精英杂交遗传策略,以期能在最少的迭代次数中寻求最优解,令算法表现出更强的适应度,也获得较高的收敛精度.
首先,对局部最优解按照适应度由优至劣排序后记为 P=[f1, f2, …, fl], 取前k名组成“精英”,记为 K=[f1, f2, …, fk], 个体间的差异系数为
ε=|f(i+1)-fi|(18)
其中, f(i+1)和 fi分别为两个不同个体的适应度.
在算法迭代过程中,利用如式(19)的杂交因子α, 将保留的“精英”在杂交池中杂交g代,并用后代更替父代,以保持种群数目不变.
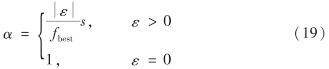
其中, fbest为最佳适应度值.可见, 个体间的差异系数ε越大,对精英后代的影响程度越大.
通过对传统SOA进行多策略融合改进,提出了改进后的FISOA寻优算法,具体步骤为:
1)设定迭代次数初始值t=0.
2)在可行解域随机产生s个初始位置.
3)子群体分配.将全体s划分为相互独立的g个子群体空间,每个子群体中包含l个个体,建立g×l维的子空间矩阵 X.
4)在杂交池中按照式(18)和式(19)进行精英杂交并产生多组精英后代.
5)计算每个搜索位置的适应度值.
6)执行多人协同搜索策略,在各个子空间内,搜索者同时计算个体i在j维的搜索方向 di, j(t)及步长 αi, j(t), 并根据自适应搜索速度vi, j(t)进行动态调整.
7)判断终止条件.当适应度或迭代次数达到设定值时跳出循环,并输出寻优结果; 否则, 更新迭代次数并执行步骤2).
采用3个典型测试函数Sphere、Schaffer和Rastrigin(函数表达式及参数设置请扫描论文末页右下角二维码查看表S1)对算法进行验证.记录PSO、SOA与FISOA算法对3个函数各运行50次后的平均最佳适应度值、平均收敛次数和达到最佳适应度的平均迭代次数,如表1,适应度迭代过程如图1所示.分析表1和图1可知,多数情况下 FISOA的性能比PSO和SOA算法表现更优,收敛曲线更平滑,收敛速度明显提高,同时具有更好的全局搜索性能,且适应度更强.
AP-FISOA-RBF模型的用电负荷预测算法流程如图2.首先,对天气信息、日期类型和历史负荷数据进行相关性分析,选取特征向量作为AP聚类的输入,获取AP聚类结果.然后,利用AP相似日理论,选取与预测日相关性较强的前n组AP聚类簇作为历史相似日,建立对应的FISOA-RBF神经网络相似日选取训练集并进行训练.最后,输出n个第i簇相似日预测值yi的加权求和结果Y作为最终实际预测值,即

其中, φi为预测权值, φi=ri/∑ri; ri为相关系数.
在算法迭代的过程中,以RBF神经网络的中心 C、 宽度 B和权值 W建立初始搜索种群 x=[c1 b1 w1 c2 b2 w2 … cm bm wm], 寻求最小适应度下的最优解作为网络参数.以误差函数最小建立的适应度函数为
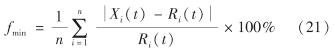
其中, Xi(t)和Ri(t)分别为第i次数据采集得到的电力负荷的预测值和实际值; n为预测时刻个数.
分析FISOA-RBF模型的适应度变化曲线(请描论文末页右下角二维码查看图 S1)可知,融合策略的引入,保持了随机解的稳定性,能够更快更准确地寻求RBF参数的全局最优解,使得RBF获得更好的学习速度和精度.
以中国西安市某大型公共商业建筑为研究对象,采集2019- 09- 01—2019-10-21共1 224组用电负荷、日天气信息和日类型信息的标准化数据,并以2019-10-21为预测日,使用AP-FISOA-RBF模型仿真预测当天的用电负荷.其中,取前1 200组数据用于网络训练.预测模型的固定参数请扫描论文末页右下角二维码查看表S2,不同模型的参数训练方式请扫描论文末页右下角二维码查看表S3.
AP相似日选取的首要任务是选择合适的特征向量.首先,对天气和日期类型等定性指标进行数据量化,并归一化至[0, 1].然后,利用皮尔逊系数法分析量化后的数据,获得影响建筑用电负荷的主要特征参数,如表2.选取系数较大的特征向量作为AP聚类与预测网络的输入,分别为历史日用电负荷(U1)、 日平均温度(U2)和日期类型(U3), AP聚类的输出为AP簇(P), 预测网络的输出为预测日用电负荷(Y).
AP相似日选取包括AP聚类与相似日的选取.输入历史日负荷、日平均温度和日期类型3个特征向量,采用AP算法进行聚类,结果如图3和表3,得到8组放射状AP聚类结果,同组聚类点之间具有显著相似性.相似日编号为[1, 2, …, 50],分别代表历史日[2019- 09- 01, 2019- 09- 02, …, 2019-10-20].
将主要影响用电负荷的日平均温度(U2)和日类型(U3)作为2个特征向量,结合表3,利用皮尔逊系数法筛选与预测日相关性较高的前5组AP簇,即分别为AP8、AP7、AP1、AP6和AP3对应的相似日,从而完成相似日选取.
本研究采用平均绝对百分比误差(mean absolute percentage error, MAPE)和预测均方误差(mean square error, MSE)两个指标对预测模型进行评价,计算式分别为

其中, Xi和Ri分别为第i次采集数据的电力负荷的预测值和实际值; r为样品采集次数.预测模型的MAPE值越小表明模型的预测精度越好.
本研究基于AP-FISOA-RBF模型预测2019-10-21的建筑物短期用电负荷.结合表2设置RBF神经网络为3- 8-1结构,即网络输入层神经元个数n=3, 隐含层数目m=8, 输出层神经元个数k=1.结合表3,对AP8、AP7、AP1、AP6和AP3这5组AP相似日的数据进行训练,确定FISOA-RBF模型的相似日预测权值,计得实际预测值为
Y=0.28y1+0.21y2+0.17y3+0.17y4+0.16y5(24)
网络参数训练结果如表4.由表4可见,与传统RBF、SOA-RBF和PSO-RBF模型相比,训练后的AP-FISOA-RBF神经网络能够很好的逼近该非线性时间序列,逼近能力较高,也更易获得最佳运行效果下的最优解.
图4 RBF、PSO-RBF、SOA-RBF和AP-FISOA-RBF模型的建筑电力负荷日预测结果
Fig.4 (Color online)Comparison of daily load forecasting results based on RBF、PSO-RBF、SOA-RBF、AP-FISOA-RBF mode
图4和图5为采用RBF、PSO-RBF、SOA-RBF和AP-FISOA-RBF算法进行建筑用电负荷预测的结果.可见,与传统的RBF、PSO-RBF和SOA-RBF预测模型相比,AP-FISOA-RBF模型的拟合度更高,预测结果更贴近真实值,MAPE值分别降低了93.05%、83.60%和71.13%,MSE值分别降低了95.30%、87.57%和73.23%.综上,采用融合策略改进后的FISOA 算法比常规PSO和SOA 算法性能更好,全局寻优性能更强,尤其是在对历史数据进行AP聚类处理后,可显著提升FISOA-RBF的预测精度.
采用聚类算法(k-means、模糊c-means和AP)和无聚类算法(AR、SVR、GM、RBF、PSO-RBF、SOA-RBF和FISOA-RBF),计算建筑用电负荷预测的MAPE值、MSE值和模型运行的耗时,结果如表5.所有结果都是运行10次后的平均值.
分析表5可知,无聚类算法处理下,RBF模型的MAPE值比其他采用单一算法模型更小,即预测结果更稳定,证明采用RBF神经网络的合理性.其中,FISOA-RBF模型的预测误差最小,更贴近真实值.可见,融合改进策略能够使FISOA算法更好地优化RBF网络参数,弥补了梯度下降法进行参数调整的不足,提高了传统RBF的预测性能.采用AP聚类后,AP-FISOA-RBF模型预测的MAPE低至0.82%,MSE低至805.17 kW2,比无聚类算法的FISOA-RBF模型降低了68.05%,明显减少了外界环境对负荷预测的影响,增强了模型的稳定性.但是,k-means和模糊c-means算法因初始聚类中心及聚类数难以设定,预测时长和误差均显著增加.
分析模型运行耗时结果发现,虽然传统的RBF模型的预测时间较长,但优化后训练速度均能得到显著提高,AP-FISOA-RBF模型的平均预测速度比传统RBF、PSO-RBF和SOA-RBF模型分别提高了54.34%、39.25%和23.96%,收敛速度显著提高.
结合SOA算法的全局搜索性能,改进后的FISOA算法可对RBF网络的中心、权值和宽度参数进行更准确有效的全局寻优.同时,AP相似日选取的应用能有效克服天气和日期类型等影响,快速且准确地处理大量样本数据.相比传统的PSO和SOA算法,采用融合策略的FISOA算法能明显优化RBF网络.自适应搜索速度和多人协同搜索模式显著加快了对RBF参数的寻优速度,精英后代遗传策略明显降低了子代种群的随机性,提高了解的质量.综上可见,本研究提出的AP-FISOA-RBF预测模型受输入影响较小,在预测精度和收敛速度上均有较好的表现,证明了模型在高精度用电负荷预测方面的有效性和可靠性.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N