作者简介:张节松(1981—),淮北师范大学副教授、博士.研究方向:保险与风险管理.E-mail:j_s_zhang@126.com
中文责编:方 圆; 英文责编:淡 紫
School of Economics and Management, Huaibei Normal University, Huaibei 235000, Anhui Province, P.R.China
probability theory; catastrophe risk; fractional compound Poisson process; moment matching method; generalized Pareto distribution; insurance bond
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.02208
中华人民共和国国务院于2014年发布《关于加快发展现代保险服务业的若干意见》(国发[2014]29号),明确保险是现代经济的重要产业和风险管理基本手段,围绕保障和改善民生,将保险纳入灾害事故防范救助体系,鼓励各地根据风险特点,探索对台风、地震、滑坡、泥石流、洪水及森林火灾等自然灾害的有效保障模式,建立巨灾保险制度.同年7月,深圳成为中国第1个巨灾保险试点,随后宁波、云南、四川、广东、黑龙江等地相继开展巨灾保险试点,巨灾保险试点工作拉开帷幕.
巨灾破坏性强,随时可能产生高额索赔.保险公司的承保能力有限,巨灾风险的合理分散直接关系到保险公司的经营稳定性与长足发展.为了转移风险并增加承保风险能力,近年来出现一种新型风险转移工具——保险连接债券[1].保险公司或再保险公司通过与银行合作,发行巨灾保险债券,搭起保险与资本市场之间的桥梁.借助资本市场的雄厚资金提高保险公司的承保能力,同时也为投资者提供一种新的投资途径[2].2015年7月1日,中国第1只以地震风险为保障对象的巨灾债券在境外市场成功发行.此类巨灾债券在逻辑特征上具有保险产品属性,结构特征上又具备金融产品属性,这种双重属性特征、巨灾风险发生频率及其造成损失规模的难以预测性,使得巨灾风险债券的估值比纯金融衍生品定价更困难,至今仍未形成统一的定价理论体系[3].
巨灾衍生品定价的一个重要因素是恰当选择巨灾损失随机模型[3- 4].经典的极值风险理论假定风险发生的时间间隔服从指数分布[1- 6],但地球物理学的现代应用研究发现,极端灾害事件发生的时间间隔具有记忆性,服从幂律分布[7-10].MUSSON等[8]研究了日本和希腊几个地区的地震间隔时间,发现对数正态分布的拟合效果更好.SALIM等[9] 采用广义Bartlett-Lewis模型与Pareto风暴到达时间间隔,研究爱尔兰西南部每小时的降雨数据.STOYNOV等[10]提出一种转换时间分布预测长江和黄河的洪水到达时刻.REPIN等[11] 运用随机过程方法考虑极端灾害事件发生时间间隔的非指数分布现象,并首次提出分数Poisson过程.BIARD等[12]进一步将索赔间隔变量的分布函数由指数分布替换为Mittag-Leffer分布,采用复合分数Poisson过程描述保险公司的盈余过程,构建了适用于巨灾冲击情形的复合分数Poisson盈余过程,并应用于破产理论.与经典的复合Poisson风险模型不同,复合分数Poisson过程为非平稳非马氏过程[12-13].BIARD 等[12, 14]研究了复合分数Poisson过程的长相依性和短相依性,WANG等[15]给出相应参数估计,SCALAS等[16]证明其二次变差过程的收敛性,ZHANG等[17]则在最大化调节系数的优化标准下研究该过程分层再保险问题.
本研究考虑巨灾冲击的影响,采用复合分数Poisson过程刻画保险公司的承保风险; 为合理分散高额索赔风险,在利用矩匹配方法给出累积损失广义Pareto型逼近分布的基础上,给出CIR(Cox-Ingersoll-Ross)利率模型下零息票巨灾债券的定价公式; 结合数值示例验证分布逼近的有效性,特别是对大额索赔情形拟合效果理想.本研究还分析记忆参数对期望风险和债券价格的动态影响,揭示不同债券期限水平下的变化趋势.研究结果可为保险公司在巨灾冲击情形下准确估测并合理转移风险、维护公司的稳定经营、以及减轻灾后恢复时政府的财政压力提供理论依据.
考虑以0时刻为起点并以T时刻为终期的保险与金融市场,其不确定性表示为带流的概率空间(Ω,F,P,(Ft)0≤t≤T). 记{Sh(t):t∈[0,T]}为累积索赔(损失)过程,其中, h为记忆参数; {Xi:i≥1}为独立同分布的随机索赔变量; {Vh(t):t∈[0,T]}为零息票巨灾债券的价格过程; {rt:t∈[0,T]}为短期利率过程; {ωt:t∈[0,T]}为标准布朗运动.
鉴于巨灾发生时间间隔分布的幂律性[7-10],本研究采用文献[12]提出的复合分数Poisson模型,刻画保险公司的承保风险过程.因此, t时刻之前保险人的累积损失Sh(t)为

其中,索赔序列{Xi: i≥1}具有共同分布FX; 计数过程Nh(t)为分数Poisson过程.具体地,设索赔间隔时间序列{τi: i≥1}相互独立且具有共同分布:
P(τ>t)=Eh(-λth)
其中, λ>0; 0<h≤1; Eh(z)为Mittag-Leffler函数,且
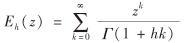
其中,z为复变量; Γ表示伽马函数. 记tn=τ1+τ2+…+τn 表示第n次索赔时刻,则索赔计数过程Nh(t)=max{n≥0:tn≤t}=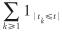 即参数为h的分数Poisson过程. {Xi: i≥1}与Nh(t)独立时,称模型(1)为复合分数Poisson模型.
即参数为h的分数Poisson过程. {Xi: i≥1}与Nh(t)独立时,称模型(1)为复合分数Poisson模型.
若h=1, 复合分数Poisson过程退化为经典复合Poisson过程.但与经典情形不同,当0<h<1时, Sh(t)不再具有马尔科夫性[13],因为该过程捕捉了非指数分布等待时间的长记忆性效应[18]; Sh(t)也不是Lévy过程,因为该过程非平稳[12].
利率是金融市场的重要价格变量之一,直接决定了相关金融产品的价格.在利率随机行为的众多刻画模型中,Vasicek和CIR单因素利率期限结构模型应用最为广泛[19-20].本研究采用含平方根形式(规避短期瞬时利率可能为负的情况)的CIR利率模型,在客观概率条件P下,将短期利率rt表示为
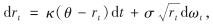
其中, κ、θ及σ均为常数,满足2κθ>σ2; dωt可看成是一个均值为0,方差为dt的正态变量,表示布朗运动在小时间内的微增量; κ为利率均值回归速度; θ为长时期利率水平; 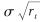 为波动率.
为波动率.
在风险中性测度Q下,利率过程变化为
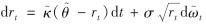
其中, 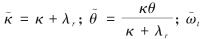 仍为一个标准布朗运动, 且
仍为一个标准布朗运动, 且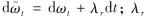 为确定利率风险的市场价格参数, 通常λr<0.
为确定利率风险的市场价格参数, 通常λr<0.
由于缺少可交易的标的资产,巨灾债券是以触发水平为变量的结构化支付产品.本研究约定以Sh(T)超过债券合约中指定的门限水平D为触发条件.考虑面值为1,期限为T的零息票巨灾债券,其支付结构PCAT(T)定义为
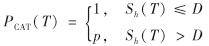
其中, p表示在期限[0,T]内累积索赔超越门限水平D条件下约定的支付比例.
给定门限水平D, 巨灾抵达过程为Nh(t), 在风险中性测度Q条件下,遵循COX等[21-22]的假定,即仅依赖巨灾风险的变量与仅依赖金融风险的变量独立,且累积索赔过程从客观概率转换为风险中性测度中保持特征结构不变.因此,CIR利率模型下期限为T、 面值为1的零息票巨灾风险债券在时刻t的价格为
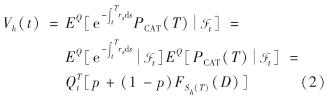
其中,第2个等号用到了巨灾与金融变量独立的假定; F为累积损失分布;  ,
,
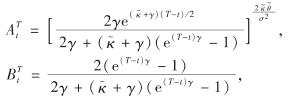
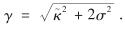
由定价公式(2)可知,要求出巨灾债券的价格过程,除确定待定参数,还需求解Sh(t)的精确分布,然而高阶卷积通常难以计算[1, 3].此类分布即使在经典复合Poisson情形下也几乎不能获得[23].在保险与金融实践中,通常运用矩匹配方法进行分布逼近.根据拟逼近分布尾部特征的不同,存在多种矩匹配的方法.当分布轻尾时,可选择混合Erlang 分布[24]; 当分布重尾时,LINDSKOG等[25-26]指出广义Pareto分布具有良好适用性.这里考虑巨灾损失分布重尾的情况,令Sh(t)服从广义Pareto分布
FS(s)=B(υ,α,s/(η+s)), s>0(3)
其中, α>0; η>0; B(a,b,x)为正则不完全Beta函数,B(a,b,x)=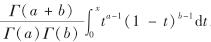 ,0<x<1,参数a>0, b>0.
,0<x<1,参数a>0, b>0.
易见, FS中含有3个待定参数υ, α及η. 实际上, S=Sh(t)的m阶矩可通过这些参数表示为
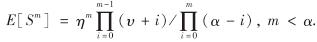
记Mk=E[Sk]/(E[S])k, 由文献[26]可知,3个待定参数又可通过S的前三阶矩表示为
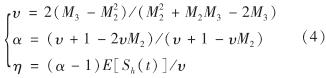
因此,根据矩匹配方法,对任意给定时刻t, 只要求得Sh(t)的前三阶矩,再由式(3)和式(4)即可求得复合分数Poisson模型的逼近分布.实际上,有如下结论.
引理1 记索赔变量X的前三阶矩为μi, i=1,2,3, 则累积索赔Sh(t)的前三阶矩分别为
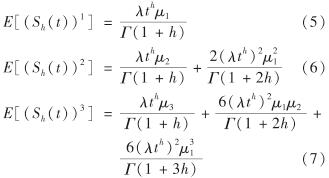
【证】 综合文献[27]的式(4.10)、(2.6)以及(1.5),可得Sh(t)特征函数为
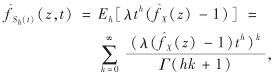
其中,  , 表示X的特征函数.将
, 表示X的特征函数.将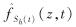 对z求导可得
对z求导可得
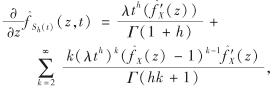
于是,

因此,由特征函数的性质可知,

式(5)成立.
将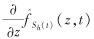 对z求导可得
对z求导可得
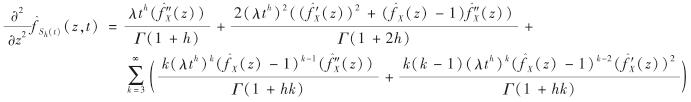
于是,
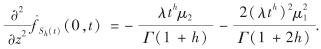
再由特征函数的性质可得,
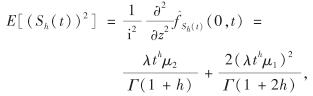
式(6)成立.
类似可证式(7)成立.证毕.
注1 随着记忆参数h的增大,期望损失可能出现递减、先增后减以及递增的多种情形,与时间参数t的大小有关,并不具有统一的单调性.
注2 由引理1可得,累积损失的方差等于
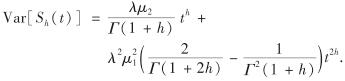
在h=1时, Var[Sh(t)]退化为λμ2t. 但当0<h<1时, Var[Sh(t)]非线性,且随着时间推移按幂律tν(ν≠1)增长,该现象被称之为反常扩散[12].
至此,根据式(3)给出如下分布逼近结果.
定理1 记Mk=E[(Sh(t))k]/(E[Sh(t)])k, 则Sh(t)近似服从广义Pareto分布
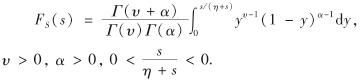
其中,参数υ, α及η由式(4)确定.
令个体索赔额X(单位:万元)服从Pareto型重尾分布
FX(x)=1-(300/(300+x))4, x>0.
给定λ=1, T=2及h=0.5, 对累积索赔Sh(T)的分布进行随机模拟(其中,分数Poisson过程的模拟方法可
参考文献[28]),并与逼近分布FS进行比较,结果如图1.
图1 累积损失的随机模拟分布与广义Pareto逼近分布图
Fig.1 Stochastic simulation distribution and generalized Pareto approximation distribution of cumulative loss
由图1可见,定理1所给出的逼近效果良好,特别是对大额索赔拟合程度非常高,这与本研究更关注巨灾索赔厚尾特性的考虑相一致.
给定利率模型相关参数κ=0.20, θ=0.10, λr=-0.01, σr=0.08, r0=0.06, 支付比例p=0.050, 市场风险参数λr=-0.01及门限水平D=300. 将期限水平T及记忆参数h∈(0,1]视作变量,考察不同期限水平下,记忆参数对期望风险和债券价格的动态影响,结果如图2.
由图2(b)可知,债券合约的期限T越长,债券价格越低,因为利率风险增多且触发条件发生的巨灾风险也越大(门限水平固定).进一步对比图2(b)与图2(a)发现,对给定的期限T, 随着记忆参数的增大,债券价格出现单调递增(T=0.2)、 先减后增(T=1.0)及单调递减(T=1.8)多种情形,并无确定的变化趋势,且与期望损失的变化情形正好相反.这符合风险与收益成正比的均衡原则,因为期望损失越大,投资者面临的风险增大,债券价格下降,期望收益提高.至于记忆参数增大的条件下,期望损失及债券价格均没有确定变化趋势的现象,主要与索赔次数有关.实际上,Mittag-Leffer型等待时间变量具有重尾特性,记忆参数h的增大可能引起索赔次数期望值的递增或递减.与传统指数型索赔等待时间不同,Mittag-Leffer型等待时间具有无穷均值.
结 语
中国是世界上受自然灾害影响最严重的几个国家之一,尽快建立合理的巨灾保险制度具有重要意义.目前,中国巨灾保险试点工作不断推进,但仍需进一步创新产品设计开发,建立多层次巨灾风险分散机制.本研究为了准确评估承保巨灾风险可能给保险公司带来的冲击,采用更贴近保险实务的复合分数Poisson模型刻画保险公司的风险过程,并考虑巨灾风险的厚尾特征,运用广义Pareto型逼近分布; 为合理分散和转移巨额损失,研究了CIR利率模型下巨灾保险连接债券的定价问题,并给出相应定价公式.结合数值示例验证分布逼近的有效性,其对高额索赔的拟合效果理想.在不同债券期限水平下,考察记忆参数对期望风险和债券价格的影响.结果表明,记忆参数的增大对期望风险和债券价格的影响呈现出相反而多形态的趋势,与期限水平密切相关.研究说明了单调性相反的现实意义,多形态趋势的原因主要与记忆参数对期望索赔次数的影响有关.然而,该影响机制的更深层次原因还有待进一步探究,可能与记忆效应的长期和短期性有关.鉴于Mittag-Leffer分布的特殊性及其非初等密度函数处理的非平凡性,要探明其确切原因还需要一些处理技术的突破,这将作为下一步研究的重要方向.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N