作者简介:张健超(1991—),深圳大学博士研究生. 研究方向:土木工程无损检测及混凝土结构耐久性. E-mail: zhangjianchao728@163.com
中文责编:坪 梓; 英文责编:之 聿
1)中国地震局工程力学研究所,中国地震局地震工程与工程振动重点实验室,黑龙江哈尔滨 150080; 2)深圳大学土木与交通工程学院,广东省滨海土木工程耐久性重点实验室,广东深圳518060
1)Institute of Engineering Mechanics, Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, China Earthquake Administration, Harbin 150080, Heilongjiang Province, P.R.China2)College of Civil and Transportation Engineering, Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Durability for Marine Civil Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong Province, P.R.China
building materials; rubber mortar; 3D-visualization; X-ray micro-computed tomography; crack propagation; image processing
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.02144
随着橡胶消费的增加,大量废弃橡胶尤其是废弃轮胎带来环境污染问题.橡胶-水泥复合材料由于可回收作为骨料来源,受到了广泛关注[1].橡胶-水泥复合材料作为一种新型的环保材料,相对于普通混凝土,具有更好的延展性、韧性、抗冲击性、能量耗散和阻尼比[2- 4],同时也有抗压强度、抗拉强度和弹性模量低的缺点[5- 8].现有研究大多是基于宏观尺寸的力学分析[9-10],对于内部介观尺寸变化和表征方面的研究较少[11].对于橡胶-水泥复合材料,受载下内部的介观裂缝可能会演变成宏观裂缝[12],从而带来严重的经济和社会损失.因此,随着橡胶 水泥复合材料的广泛应用,有必要对其内部的裂缝发展过程展开研究.
最近几年, X射线计算机层析成像(X-ray computed tomography, XCT)无损检测技术被广泛应用于橡胶-水泥复合材料的内部裂缝检测中,并且取得了较为直观的可视化结果[13-15].在处理XCT图像时,往往采用全阈值法,即根据灰度直方图划分图像灰度值,来分离固相和气相等目标[16].这种处理忽略了X射线不均匀和噪声的影响,且确定阈值范围带有较大的主观性.以局部阈值法能够解决以上问题,同时也能减小图像中伪影的影响[17].然而在识别介观裂缝时会在出现较大的尺寸误差[18].相比于普通混凝土,橡胶-水泥复合材料受压破坏时候会产生更多的介观裂缝[19-20],导致实际中得到的XCT图像更加复杂,而以往的方法也不再适用于橡胶-水泥复合材料内部裂缝的图像处理.为此,本研究建立一种比传统处理方法能更准确识别、分离橡胶砂浆内部孔隙和裂缝的方案,研究不同质量分数的橡胶砂浆内部裂缝的变化规律.
本实验采用P.O.42.5普通硅酸盐水泥(参照GB 175—2007)、去离子水和标准砂,砂子、水泥和水的质量比为4:2:1.其中,砂子选择粒径为100~300 μm的细砂,堆积密度为1 810 kg/m3.橡胶颗粒粒径为100~300 μm,堆积密度为850 kg/m3,质量分数分别为0、5%和10%.将上述材料按比例混合搅拌后浇入10 mm×10 mm×10 mm的模具中,浇筑后将样品连同模具放入(20±2)℃的标准养护室中养护24 h并拆模,再在相同条件下继续养护27 d.在XCT扫描测试开始前,用砂纸打磨样品的表面,以便可以均匀施加压力.
采用基于XCT原位的加载扫描装置.试样加载速度为0.1 mm/min,采样速率为500 ms/次.在正式加载前,进行预加载,对橡胶质量分数为0、5%和10%的样品,分别取6个试样测试相应的极限荷载(参照标准GB/T 17671—2020).得到3个不同橡胶质量分数的极限荷载后,开始正式实验.第1次扫描未加载状态的样品,然后对分别增加到50%极限载荷和90%极限载荷的载荷进行XCT扫描.最后,将样品加载到破坏状态(极限加载),停止加载并进行最后1次扫描,共扫描4次.扫描参数为:电压为80 kV,电流为100 μA,放大倍率为0.4,曝光时间为8 s,图像矩阵为1 024 voxel×1 024 voxel×1 000 voxel,像素分辨率为14.273 5 μm×14.273 5 μm×14.273 5 μm.
通过XCT原位加载得到的3D切片图像中,包含水泥、砂子、孔隙、裂缝、橡胶颗粒、未水化水泥颗粒、外部空气和伪影等.为达到分离裂缝目的,建立图1所示流程图,主要步骤为:
1)沿z方向取切片图fz0作为输入,确定图中样品边界并获得只包含样品区域部分的图像fz1(边缘含少量背景残留);
2)对fz1进行二值化处理,获得包含孔、橡胶颗粒、裂缝和少量边缘背景的二值化图fsz1;
3)通过特定的形状分离筛选出孔(除去与橡胶颗粒相同形状特征的)、橡胶颗粒、裂缝的2D二值图像Fz(Fz1, Fz2, Fz3);
4)根据Fz图像栈,堆叠成Fz3D;
5)重新沿x和y方向分别取切片图fx0 和fy0,依次按照步骤 1)至步骤 4)得到Fx3D 和Fy3D;
6)将Fx3D、Fy3D和Fz3D全部选择孔图像,其交集作为最终孔的3D图像,以同样方式得到橡胶颗粒和裂缝的图像.
在获取的XCT图像中,常常在样品区域的边缘部分存在与外部连通的裂缝或孔隙,为能区别于外部空气,需要封闭处理.对裂缝附近的灰度值进行非线性拉伸处理,构建的变换函数为
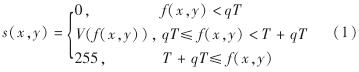
其中,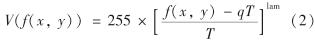
f(x,y)为原始输入图像的灰度值; T为f(x,y)的Ostu's阈值; q为区间系数,本研究取0.7; lam为系数,取0.04; s(x,y)为输出图像的灰度值.
图2以橡胶质量分数为10%的样品切片为例,进行真实的轮廓处理.除了区域A外,其他边缘线都能很好识别. 将二值化图像填充后便可得到样品区域的掩膜M(x, y), 有
g0(x, y)=fz0(x, y)×M(x, y)(3)
其中,输出g0(x,y)为只包含样品区域的灰度图像; M(x,y)中的像素值只包含0和1.为改善该图在样品区域的对比度,对样品所在区域的灰度值进行最大最小标准化,得到g(x,y), 结果如图2(c).其中,残留部分背景(外部空气)在后面孔隙筛选时会被分离.通过以上操作可获得较为真实的样品区域图像,并且区域A中的连通裂缝也被识别为样品部分,如图2(d).
Fig.2(Color online)The processing process of real contour of sample
Sauvola's方法[17]属于局部阈值法.阈值计算公式为
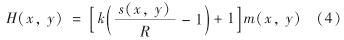
其中, m(x,y)和s(x,y)分别为像素点(x, y)的灰度平均值和标准差; k是敏感系数,本研究取0.15.可得x和y方向的图像为
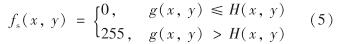
将高于局部阈值的设为前景255,其他为背景0,由式(5)可得x和y方向的2D图为
F1sz(x, y)=255×M(x, y)-fs(x, y)(6)
将表示样品区域的掩膜与二值化图像结果相减,可得到样品内部的孔隙与裂缝.
样品二值化结果如图3.在ImageJ中加载所有沿z方向的切片,选定图3所示3个黑框处,进行“Edit”和“Clear”,并应用到所有切片.经过此操作,在进行邻域标记时,残留边缘空气便与裂缝区分开.
对于图像上任意一个像素的邻域,可将其周围24个点标记为N24(P)集合.
在二值图中,如果灰度值均为255的像素点都在集合N24(P)中,那么这些像素点同属一个24连通域.本研究对图2中24连通域的标记可以通过两步法[21]在Matlab中完成.
为了能够在形状上区分裂缝、孔和橡胶颗粒,本研究建立一个形状分离器,其细长度p为
p=dmaxdmin/d2E(7)
其中, dmax和dmin分别是最大和最小Feret直径; dE为等效直径.当连通域为圆形时, p=1; 当连通域为正方形时, 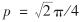 ; 当连通域为正三角形时, p=π/2; 当连通域为长方形(长为a,宽为b)时,
; 当连通域为正三角形时, p=π/2; 当连通域为长方形(长为a,宽为b)时,  .
.
等效直径dE为

其中, s为连通域的面积.
连通域中心点(xo, yo), 为每个连通域内所有像素点坐标的平均值.
橡胶颗粒的粒径范围为100~300 μm,形状介于圆形和正三角形之间,即细长度在[1,π/2]内.具体参数筛选条件如表1.
表1中,若条件2的两个条件都满足,便判定为橡胶颗粒(包含部分孔).条件1中的xmin、 ymin、 xmax和ymax分别对应图像中连通域中心点坐标的最值; t为判定是否靠近外侧的阈值条件,本研究取15.
根据以上条件和参数,建立形状筛选过程(图4),步骤为:
1)将上述领域标记图像fz作为输入,并构建与之相同的副本fz1, 分别填充fz1中每个邻域中的空洞并得到图像Q12;
2)分别计算图像fz和Q12的形状系数,得到U1和U2, 计算中保持连通域编号不变,那么每个连通域都有U1和U2;
3)当U1不满足条件1,判定为边界外部空气残留,将之全部剔除,得到图像Q2; 当U1满足条件2时,判定为橡胶颗粒以及相同形状的孔,将之全部从Q2中筛出,得到剩余图像Q3; 当U1满足条件3时,判定为孔,并将其全部筛选出,剩余图像为裂缝.
以橡胶质量分数为10%的样品为例,加载下的图像处理结果如图6.通过相同的处理过程,可以得到不同加载阶段3种质量分数橡胶的裂缝3D重构图,计算体积与宽度,分析不同质量分数橡胶对试样内部裂缝的影响.
不同橡胶质量分数试样在不同加载阶段的裂缝体积如图7.试样内部的裂缝体积变化趋势是一致的.试件破坏前裂缝体积较小,在极限荷载作用下突然增大.在加载前,试样内部初始裂缝的体积随着橡胶的掺入逐渐增大,这是因为橡胶-水泥界面的作用效果一般不如传统的橡胶-砂子界面,橡胶的掺入可能会改变橡胶砂浆内部初始结构的特征,导致初始裂缝体积的增加.但试样破坏时,橡胶质量分数为0的试样裂缝体积最大(约为橡胶质量分数为10%试样的2倍),其次为橡胶质量分数为5%的试样. 这是因为橡胶是一种可逆形变的高弹性材料,它的掺入提高了试样整体对输入能量的吸收,进而提高试样的延性,导致破坏时裂缝体积的减小.
图7 不同橡胶质量分数试样在不同加载阶段的裂缝体积
Fig.7 The crack volumes of the samples with different rubber contents at different loading stages
裂缝体积分数随裂缝宽度的变化如图8. 由图8可见,随着橡胶掺入量的增加,试样内部的细裂缝逐渐增多,宽裂缝逐渐减小.
结 语
改进传统方法,进行橡胶砂浆受载后裂缝的识别和提取研究.提出的方法能够较精准地提取XCT加载测试中橡胶砂浆样品图像的裂缝,并完成橡胶颗粒和孔的分离.在加载前,试样内部初始裂缝体积随着橡胶的掺入逐渐增大,试样破坏时,由于橡胶提高了试样受载后的延性,导致裂缝体积随着橡胶质量分数的增加而减小.随着橡胶掺入量的增加,试样内部的细裂缝增多,宽裂缝逐渐减少.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N