作者简介:杨亚红(1976—),兰州理工大学副教授、博士.研究方向:水质净化机理. E-mail: yangyahong@Lut.cn
中文责编:晨 兮; 英文责编:之 聿
1)兰州理工大学土木工程学院,甘肃兰州730050; 2)清华大学深圳研究生院,广东深圳518055
1)College of Civil Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, P.R.China2)Shenzhen Graduate School of Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, Guangdong Province, P.R.China
sponge city; Kriging interpolation; semi-variation model; cross-validation; fitting model; radial flow; low impact development(LTD); waterlogging
DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1249.2021.01027
为探索中国兰州市某高校校园雨水管网节点积水深度的主要影响因子,以研究区域雨水管网246个节点在降雨重现期(P)为7 a和50 a时积水深度的数据为例,利用ArcGIS统计模块分析2个重现期降雨下的节点积水深度数据的空间差异性,采用交叉验证法对比研究4种Kriging插值模型(稳定、球形、高斯与指数模型).由Pearson相关性分析结果可知,2种重现期的积水情形下节点最大深度与积水深度相关性均较强,相关系数分别为0.605和0.766. 4种Kriging半变异函数模型的预测值与实测值的对比结果表明,高斯模型的偏差均值(Kriged reduced mean error, KRME)最小(P=7 a时,KRME=-0.87×10-4; P=50 a时,KRME=0.87×10-3),一致性系数(Kriged reduced mean square error, KRMSE)最优(P=7 a时,KRMSE=0.939; P=50 a时,KRMSE=0.947),确定该研究区域节点积水深度Kriging插值方法最适宜的模型为高斯模型.研究结果可为利用研究区域有限的内涝数据更有效地识别积水内涝提供方法,同时为内涝的控制和消减措施提供理论基础.
In order to explore the main influence factors of the node water depth of rainwater pipe network located in a campus in Lanzhou city and to study the interpolation method suitable for the node water depth data, we analyze the data of the water depth of 246 nodes of the rainwater pipe network in the study area under the rainfall return periods of 7 years and 50 years(i.e., P=7 a and P=50 a, respectively). Using ArcGIS software, we make spatial difference analysis of node water depth data of rainfalls in the two return periods, and conduct a comparative study on the four Kriging interpolation models, i.e. stable model, spherical model, Gaussian model and index model, by means of cross-validation method. The results show that the Pearson correlations between the maximum depth of nodes and the depth of water accumulation for P=7 a and P=50 a are strong, and the correlation coefficients are 0.605 and 0.766, respectively. Through comparing the predicted values with the measured values of four Kriging semi-variation function models, it is found that the Kriged reduced mean error by Gaussian model is minimum(KRME=-0.87×10-4 at P=7 a and KRME=0.87×10-3 at P=50 a), and the Kriged reduced mean square error is the best(KRMSE=0.939 at P=7 a and KRMSE=0.947 at P=50 a). The Gaussian model is determined as the most suitable model for Kriging interpolation method of node water depth in the study area, which provides a more effective method to identify water logging in the study area by using limited waterlogging data, and provides a theoretical basis for the control and reduction measures of waterlogging.
随着全球气候变化加剧,突发性强降雨引发的城市内涝问题日趋严重,给人们的生命财产和社会经济发展构成巨大威胁[1].据统计,2008—2018年期间,中国平均每年因洪涝灾害死亡人口约为760人,直接经济损失为2 119.50亿元[2].对暴雨引发的城市内涝进行风险评估,可针对性地进行预防和治理,是降低城市内涝灾害损失的一条有效途径.
国内外对于洪涝灾害风险评估的研究较多.BENITO等[3]综合古代洪水信息(100~10 000 a)、历史洪水数据(1 000 a)以及水文站数据(30~50 a),提出了基于历史洪灾数据的洪水风险评估方法,并将其应用于欧洲国家.WASHAKH等[4]综合分析1990—2018年Arun流域49个冰湖的冰湖溃堤洪水(glacial lake outburst flood, GOLF)的气温、降水趋势与所记录GLOF事件发生的相关性,提出了一种简单易行的GOLF风险评估模型.20世纪初,随着地理信息系统(geographical information system, GIS)的不断发展,基于情景模拟的综合性风险评估与分析开始受到普遍关注.应用该方法时,给定灾害初始条件,根据灾害演化机理进行模拟推演,得到灾害的发展演化过程,从而估计灾害损失.该分析方法能反映出灾害的动态演化,并对以前从未发生过的非常规灾害进行后果评价,其评估对象涉及多个方面,可预测建筑物、经济与社会等各方面的损失情况.AMEER等[5]利用情景模拟演化的方法对水土评估模型(soil and water assessment tool, SWAT)的模拟精度进行改进.此外,国内学者也尝试开展了一些基于情景模拟的洪涝灾害风险评估.尹占娥等[6]基于情景模拟的方法针对上海市静安区小尺度暴雨内涝进行了风险评估.胡蓓蓓等[7]根据未来规划,对天津市滨海新区2020年的暴雨内涝风险进行了预测评估.
为使评估结果更接近实际,评估的时空精细化程度能够达到事半功倍的效果.如何提高评估的时空精细化,成为目前风险内涝灾害评估的发展趋势.目前,该模拟评估方法主要针对沿海城市小尺度流域研究较多,而针对内陆地区研究较少且不够深入.本研究建立一种基于暴雨洪水管理模型-地理信息系统(storm water management model with geographic information system, SWMM-GIS)的水文学模型的城市内涝情景模拟风险评估方法,以中国西北地区某校园节点积水数据为例进行内涝风险评估,模拟该地区在特定重现期降雨情景下的城市内涝分布,并对可能造成的灾害损失情况进行分析.旨在筛选出适合于该区域的内涝插值模型方法,为利用有限观测点更有效地识别出内涝区域分布提供基础.
降雨径流模型考虑降雨的物理过程,通过水力学公式可计算降雨引发内涝的时空分布,而且模型对城市降雨积水的具体特征做了大幅简化,在保证一定的计算精度的前提下大幅降低了计算时间.目前,世界范围内有许多可用的城市降雨径流模型,例如,SWMM和伊利诺城市排水区域模拟(Illinois urban drainage area simulator, ILLU-DAS)等[8].这类模型基本可以满足城市暴雨排水系统模拟的需要.但由于是一维水动力模型,所以不适合做内涝评估分析.
Kriging插值法的提出为内涝时空分布评估提供了可能.该方法通过对积水点采样数据及地理特征合理分析其可能出现的演化过程,进而选择合适的拟合模型创建淹没分析图.Kriging插值方法不仅能量化已知点之间的空间自相关性,并可说明采样数据在预测区域范围内的空间分布情况[9].
与反距离权重法类似,Kriging插值法对周围的测量值进行加权以得出未测量位置的预测.其计算公式[10]为
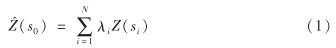
其中, si为第i个积水点位置; Z(si)为第i个位置的测量值; λi为第i个位置处的测量值的未知权重; s0为预测位置; N为测量值数.
1)半变异函数及拟合模型:Kriging法插值过程中,有限积水点扩散区域化模型是随机且规律性的.因此,模型建立需要由合适的半变异函数实现从有限至区域化的相似扩散演化,使半变异函数曲线与积水点数据达到拟合,最终用于模型预测.
半变异函数计算公式[11]为
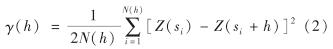
其中, h为距积水点si的距离; γ(h)为h处的积水深度变异函数; N(h)为分割距离为h时样本点的总个数; Z(si)、 Z(si+h)分别为积水点si和si+h处的积水深度测量值.
2)半变异函数的模型优选:Kriging法中,式(2)只能反映出积水点深度本身的变异特征和空间分布,不能反映出在不同空间滞后距离上的空间变异特征以及积水点的空间异质性定量化特征,故需要通过常用半变异函数的拟合模型对已知数据点离散关系进行拟合[11].拟合模型由半变异函数根据已知测量点的空间自相关性确定,如图1[12].目前常用的半变异模型有稳定、球面、指数和高斯模型等.选择合适的拟合模型是空间插值的前提条件,直接影响空间插值的精度结果.
图1 半变异函数拟合曲线示例[12]
Fig.1 Examples of semi-variation fitting curves[12]
图1中的C0是块金值,为半变异函数曲线在γ(h)轴上的截距,表示积水深度受到随机因素影响的空间变异; C为偏基台值,即半变异函数值达到稳定时的增量,用于反映积水深度因空间结构引起的变异; C0+C为基台值,表示积水深度总的空间变异; C0/(C0+C)为基底效应,表示空间的变异特征,该值越大,说明积水深度的空间变异更多是由随机成分引起的; a为变程,即半变异函数第1次达到稳定时所对应的采样距离,表示积水深度的空间自相关范围.
最优模型主要通过无偏性和一致性来判断.前者常采用偏差均值(Kriged reduced mean error, KRME)指标来衡量; 后者则采用一致性系数(Kriged reduced mean square error, KRMSE)指标判定.KRME越接近0,表示无偏估计的效果越佳.KRMSE越接近1,表示模型越好[9,12].KRME与KRMSE计算公式分别为
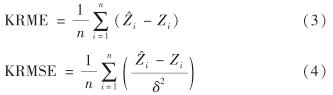
其中, 为第i个测量点的实际值; Zi为第i个测量点的估计值; n为测量点数目; δ为实际值的标准偏差.
为第i个测量点的实际值; Zi为第i个测量点的估计值; n为测量点数目; δ为实际值的标准偏差.
3)检验方法:为保证插值精度,在模型优选的基础上进一步采用交叉检验(cross-validation)进行插值方法验证.原理是在给定的样本模型中汇总之后留出部分样本用于建立模型进行预测,并求出这小部分样本的预测误差[9].
研究区域地处兰州市靠近黄河南岸的七里河区,如图2.该城区位于市内中南部,地理坐标为103°36″E—103°54'54″E,35°50'32″N—36°06'12″N.地势南高北低,平均海拔2 321 m.南部为石质山地,地形特征为山高、谷深、坡陡,岩石裸露.七里河区境内属大陆性半干旱气候.主要特征是:四季分明,冬夏长,春秋短.雨热同季,垂直气候变异显著.气温、热量和光照随海拔由南向北升高; 年平均降雨量为327 mm,由南到北逐渐降低.校区占地87 hm2,在开发之前多为平顶屋面,其数量少且占地面积有限; 周围多分布山杨、桦树群体及少量灌木.这类植物渗透系数高,对水分蒸散与入渗作用显著.校园开发后土地利用类型多样化,其中,绿地面积占比为42%,不渗透面积占比为57%(包括新开发地块4%、建筑物10%、开阔空地14%和道路29%).
利用校园雨水管网计算机辅助设计(computer aided design, CAD)图将研究范围划分为子汇水区226个.经统计,研究区域概化管道总长为8 804.55 m,汇水区总面积64.11 hm2,概化结果如图3.
因缺乏兰州市历年降雨气象水文资料,所以本研究降雨数据由暴雨强度公式生成,该公式由王杰等[13]根据兰州市国家基本气象站1960—2014年的降雨资料,通过皮尔逊-Ⅲ型分布拟合得出.降雨强度公式为
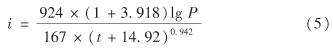
其中, i为降雨强度(单位:mm/min); P为降雨重现期(单位:年); t为降雨历时(单位:min).在该模型中,采用芝加哥降雨模式描述降雨过程.这种降雨模式可以概括大多数降雨类型,能反映出地表径流与出流量峰值,因此适用于区域和雨水系统设计的预评价[14].研究中采用雨峰系数为0.291,其主要目的是分析早期降雨高峰对研究区域径流和积水的影响.选取1、2、5和7 a重现期(降雨历时短,为2 h)和10、20、30和50 a重现期(降雨历时长,为12 h)绘制芝加哥降雨过程线如图4.本研究中实测降雨数据采用2018年6月、7月及2019年6月、7月共4个月的降雨特征和对应的流量数据,降雨编号依次为201806、201807、201905和201907(表1).
基于以上数据,将降雨数据导入率定后的SWMM模型中,模拟得到每个重现期下的雨水井节点积水数据.分别取短历时和长历时下重现期最大(P=7 a与P=50 a)时的积水情形进行基于Kriging 插值的内涝情景模拟,分析其可能出现的积水分布情况.
雨水管网中,管网节点(雨水井)的内涝积水情况与雨水井的分布、内底高程及最大深度和井内污染物的空间浓度分布等因素密切相关.不合理的雨水井及管道的空间布置不当均会损坏管网,造成局部区域的内涝积水与污染[15-16].选取与影响积水深度相关的节点内底高程与节点最大深度等节点结构属性变量,利用SPSS 19.0软件进行Pearson相关性分析,得到研究区域P=7 a与P=50 a节点积水的主要影响因子相关性大小(表2).其中, E为节点内底标高; H为节点最大深度; Q1为P=7 a时节点积水深度; Q2为P=50 a时节点积水深度.结果表明,与内底标高对积水深度的影响程度相比,节点最大深度对积水深度影响更大.重现期为7 a和50 a的积水深度标准差分别为1.034和1.043,它们分别与节点最大深度的标准差均非常接近; Pearson相关性系数分别为0.605与0.766,均大于0.5.分析其原因:重现期为7 a(短历时)和50 a(长历时)下降雨量分别达到28.33 mm和61.03 mm,按照气象学上对降雨的划分属于大到暴雨[17-18].当降雨强度最大时,到达地面形成地表径流可能在校区南高北低的地势作用驱使下直接汇入雨水管网并到达节点的最大深度,加上后续径流的持续补充,导致节点可以在短时间内保持着与最大深度相差无几的积水深度,情况严重时可能出现溢流现象.
通过节点积水影响因子Pearson相关性分析,选用节点最大深度作为节点积水深度的主要影响因子,基于校园数字高程模型(digital elevation model,DEM)进行Kriging插值情景模拟.
通过对原始节点积水深度数据进行统计分析,并绘制出正态分布图,见图5.由图5可知, P=7 a与P=50 a时的节点积水深度数据均存在明显的线性关系且基本符合正态分布. P=7 a重现期下211个积水节点深度变化为0~5.40 m,平均深度为1.39 m; P=50 a重现期下220个积水节点深度变化范围为0~5.38 m,平均深度为1.50 m.此外,同一降雨情境下易发生积水的节点多集中在深度较浅的范围内: P=7 a时,积水深度为0.76~1.52 m内有87个积水节点,占比39.4%; P=50 a积水深度在0.81~1.62 m内有127个积水节点,占比57.7%.结果表明雨水管网节点深度设置不恰当,容易造成局部区域大面积积水.
通常在Kriging插值模型方法的选择中,半变异函数作为统计采样点间的距离函数,其步长直接反映插值精度[14,19].基于以上统计分析,利用ArcGIS10.4中空间分析工具确定点与相邻元素之间的平均距离,保证参与计算的半方差的的点对数不少于30.针对P=7 a与P=50 a降雨情境下的节点积水深度数据,分别构建稳定、球面、指数与高斯4种半变异函数模型,并计算各自的特征参数进行模型优选对比.其模型参数如表3所示.
通过模型拟合对比分析,在两种降雨情境下得到的积水深度数据中,模型曲线与实际值平均化拟合度较好的均为高斯模型.在表3的模型参数分析中,高斯模型的KRME值较其他模型最接近0,其KRMSE值最接近于1.
综上所述,4个待选拟合曲线待选模型中,高斯模型最适合P=7 a和P=50 a降雨情境下的节点积水深度数据做插值研究,故优选高斯模型.
为检验高斯模型用于研究区域节点积水深度Kriging插值模拟的预测精度,在ArcGIS10.4的地统计模块中将研究区域P=7 a与P=50 a的246个节点积水深度数据随机构建为2个子集要素:65%(N=160)的数据作为训练数据集,35%(N=86)的数据作为测试数据集.以进行节点的预测值与实测值的交叉验证分析,得出研究区域节点积水深度的空间插值结果的预测值与实测值散点分布(图6).据图6,两个重现期降雨下的节点积水深度测量值与预测值拟合效果均较好,相关系数R2分别为0.784和0.857.拟合曲线(蓝色线)与1:1标准直线相差不大.通过将原始数据观测值和交叉验证所得到的预测值进行分析比较,发现在考虑节点最大深度为主要因素时,通过Kriging高斯模型插值, P=7 a预测节点积水深度均值为1.395 m,实测节点积水深度均值1.396 m; P=50 a预测节点积水深度均值为1.655 m,实测节点积水深度均值1.654 m.研究结果表明,在考虑节点最大深度因素的Kriging插值模拟高斯模型预测可取得较好的拟合效果.
选用高斯Kriging插值模型对研究区域P=7 a和P=50 a节点积水深度数据进行空间插值模拟(图7).从图7可以看出,两个重现期下节点积水深度变化范围基本一致,分别为0.627~7.577 m与0.639~8.100 m.在空间上呈现东北与西南向积水分布较良好,东南与西北向积水分布较严重,这可能是高强度降雨下,东北与与西南方向的管网布置较稀疏且均是管径较小的管段,而东南与西北方向的管网布置较密集且均是管径较大的干管及排放口排放高重现期形成的即时径流量累积导致的.此外,图8中西北方向积水深度红色区域逐渐扩大,且绿色区域逐渐被黄色区域占据,开始向红色区域过渡,呈现出绿色区域先快后慢的减少,而红色区域先快后慢的扩大趋势.这很可能是因为高重现期早期较大强度降雨使管径偏小的管段达到满载负荷状态,使得研究区域地势较低容易积水的地方出现内涝.
1)通过对兰州市某校区雨水管网P=7 a和P=50 a节点积水深度数据进行Pearson相关性分析,结果表明:与节点内底标高对节点积水深度的影响程度相比,节点最大深度对节点的积水深度影响更大.其Pearson相关系数分别为0.605(P=7 a)和0.766(P=50 a),从而确定节点最大深度作为积水深度插值模拟的主要影响因子.
2)针对原始积水点数据构建稳定、球形、高斯和指数模型进行半变异函数模型的优选及空间差异统计分析,发现在两种降雨情境下得到的积水深度数据中,模型曲线与实际值平均化拟合度较好的均为高斯模型.在模型参数分析中,高斯模型的偏差均值较其他模型最接近0(P=7 a时KRME=-0.87×10-4; P=50 a时KRME=0.87×10-3),其一致性系数最接近1(P=7 a时,KRMSE=0.939; P=50 a时,KRMSE=0.947).
3)通过Kriging高斯模型插值,两个重现期下节点积水深度变化基本处于0.627~8.100 m内,且呈现东北与西南向积水分布较良好,东南与西北向积水分布较严重.同时积水深度红色区域逐渐扩大,绿色区域逐渐被黄色占据,开始向红色区域过渡.
4)在雨水管网中,节点(雨水井)积水内涝除了与节点内底高程和最大深度等节点本身的结构属性变量有关外,可能还与大气湿度、气温、环境等因素密切相关.因此,为使得插值结果更加精确化,可考虑适当引入上述环境因子进行空间插值.
5)通过对常规开发情景下的研究区域进行节点积水模拟,得到不同降雨重现期下节点积水情况,结果表明局部区域存在内涝风险.对于这种局部内涝问题,国内传统的思想是“以排为主”,即采取加大管道管径,提高排放能力的措施来解决.但随着新型雨洪管理理念的引入,低影响开发理念越来越多地应用在城市建设中.本研究为LID措施的开展提供一定的理论基础,可以通过对比不同的LID措施对于研究区域雨洪控制的影响,筛选出最佳的LID措施组合来降低局部内涝的风险.
深圳大学学报理工版
JOURNAL OF SHENZHEN UNIVERSITY SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
(1984年创刊 双月刊)
主 管 深圳大学
主 办 深圳大学
编辑出版 深圳大学学报理工版编辑部
主 编 李清泉
国内发行 深圳市邮电局
国外发行 中国国际图书贸易集团有限公司(北京399信箱)
地 址 北京东黄城根北街16号
邮 编 100717
电 话 0755-26732266
0755-26538306
Email journal@szu.edu.cn
标准刊号 ISSN 1000-2618
CN 44-1401/N